Polymer Congress 2018
Polymer Sciences
ISSN: 2471-9935
Page 28
June 04-05, 2018
London, UK
4
th
Edition of International Conference on
Polymer Science and
Technology
R
ecent progress in supramolecular chemistry leads to
unparalleled control over the composition and shape
factor of colloidal systems. Among them, the design of
hollow capsules is a new expanding area of physical-chemical
research. Herein, we report on the preparation of ultra-
low sized (<100 nm in diameter) biodegradable polymeric
capsules for potential applications as nanocontainers in
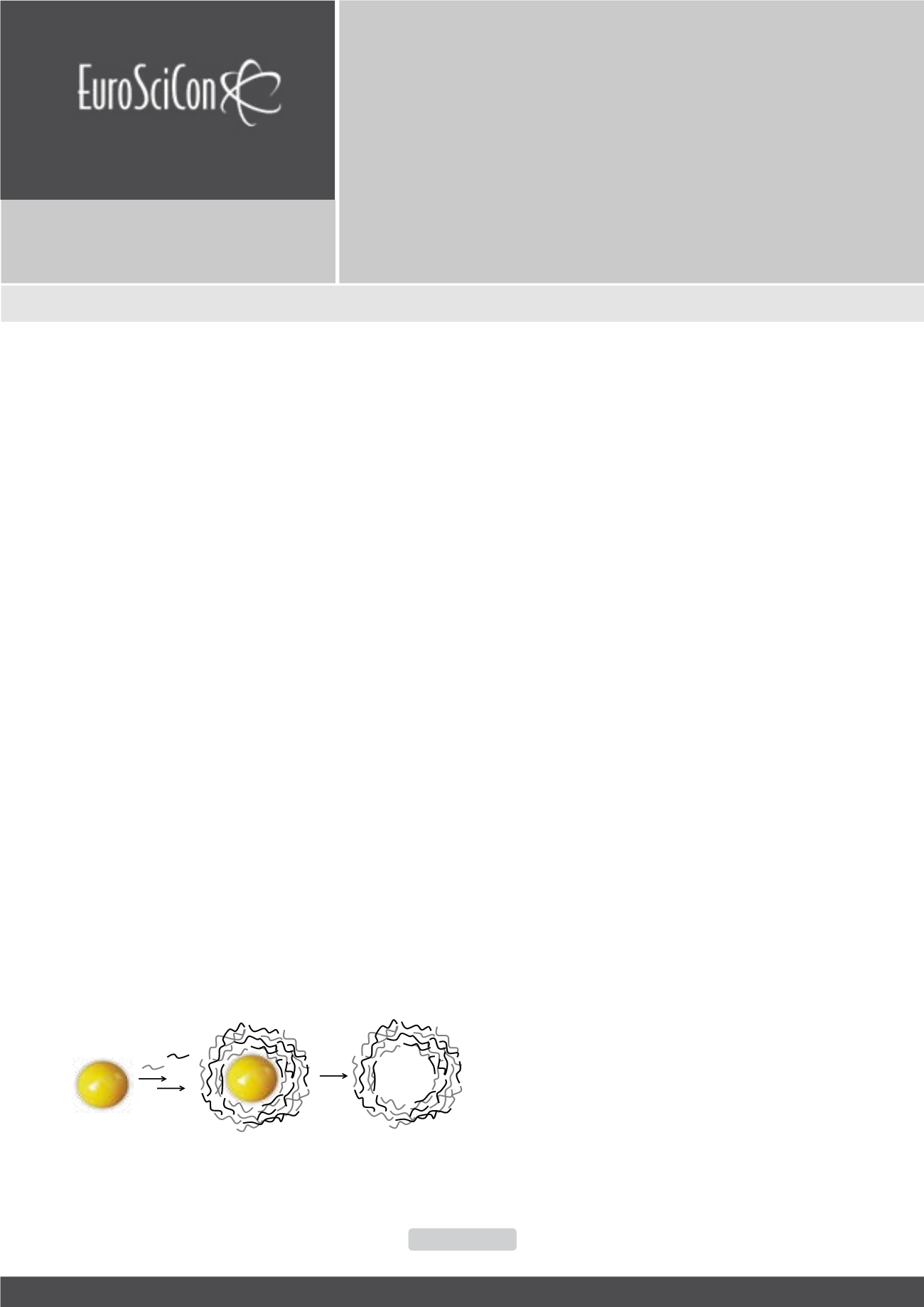
antibiotic therapy. Hollow nanospheres based on the chitosan/
poly (acrylic acid) pair are elaborated via (i) the layer-by-layer
technique using gold nanoparticles (20 and 60 nm in size) as
sacrificial templates, (ii) loading with amoxicillin, a betalactam
antibiotic, and (iii) removal of the gold core via cyanide-
assisted hydrolysis. Size, dispersity and concentration of the
resulting nanocapsules are easily fixed by the nanoparticle
templates, while wall thickness is controlled by the number of
polyelectrolyte bilayers. Electrostatic interactions between the
protonated amine groups of chitosan and the carboxyl groups
of poly(acrylic acid) act as the driving attraction force allowing
easy and fast design of robust and well-ordered multilayer
films. Successful hydrolysis of the gold core is evidenced by
time-dependent monitoring of the gold spectroscopic signature
(absorbance at 519 nm and 539 nm for the gold nanoparticles
with 20 and 60 nm, respectively). Crosslinked capsules are
also prepared through crosslinking of the chitosan chains
with gluteraldehyde. Chitosan-based nanocapsules are finally
evidenced to be promising drug delivery vehicles of amoxicillin
trihydrate with tuneable properties such as entrapment
efficiency in the range of 62-75% and 3.5-5.5% concerning the
drug loading. The drug-loading content was up to 5%.
Recent Publications
1. Peyratout C S and Dahne L (2004) Tailor-made
polyelectrolyte microcapsules: from multilayers to
smart containers. Angewandte Chemie. 43:3762-
3783.
2. Borges JOandMano J F (2014) Molecular interactions
driving the layer-by-layer assembly of multilayers.
Chemical reviews. 114:8883-8942.
3. Nguyen T T T et al. (2017) From the functionalization
of polyelectrolytes to the development of a versatile
approach to polyelectrolyte multilayer films with
enhanced stability. Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
5(46):24472-24483. Doi:10.1039/C7TA06855G
4. Belbekhouche S et al. (2018) Glucose-sensitive
polyelectrolyte microcapsules based on (alginate/
chitosan) pair. Carbohydrate Polymers. 184:144-153.
5. Jiang H X, Ding Y, Chen Q and Yang C (2004)
Core‐template‐free strategy for preparing hollow
nanospheres. Advanced Materials. 16:933-937.
Biography
Sabrina Belbekhouche is an Associate Professor (East Paris Institute of
Chemistry And Materials Science/ University of Paris, France). Her core
expertise is in polymer science, macromolecular assembly and surface
modification. This includes the polymer synthesis; the study of the physi-
cal chemistry of surfaces/interfaces; and the use of controlled assembly
at the sub-micrometer scale (nanoparticle, nanocapsule.) as well as stim-
uli-responsive systems. Current applications of her research are mainly for
biological application.
belbekhouche@icmpe.cnrs.frPromising tailor made nanocapsules based on biopolymer for
antibiotic therapy
Sabrina Belbekhouche, Ones Mansour
and
Benjamin Carbonnier
ICMPE (UMR7182), France
Sabrina Belbekhouche et al., Polym Sci 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.4172/2471-9935-C2-011
Figure 1:
Schematic illustration of hollownanocapsule elaboration by the polyelectrolyte
layer by layer self-assembly strategy. (NP: nanoparticle).
Au
hollow
NP
-
-
-
+
+
+
Au