Efficacy of Kegel Exercise vs. Lower Limb Plyometric Strengthening Exercise on Symptoms Associated with Stress Urinary Incontinence
Murugaraj T1*, Sabarish HN1, Ashila A1, Arunachalam R2, Muralidharan CK2 and Shanmugananth E1
1Department of Physiotherapy (mgmcri), Sri Balaji Vidyapeeth, Puducherry, India
2Department of Physiotherapy, mgmcri, Puducherry, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Dr. Thiyagarajan Murugaraj
Department of Physiotherapy (mgmcri)
Sri Balaji Vidyapeeth
Puducherry, India
Tel: + 9328456980
E-mail: booouk@gmail.com
Received Date: July 01, 2021; Accepted Date: October 04, 2021; Published Date: October 25, 2021
Citation: Murugaraj T, Sabarish HN, Ashila A, Arunachalam R, Muralidharan CK (2021) Efficacy of Kegel Exercise vs. Lower Limb Plyometric Strengthening Exercise on Symptoms Associated with Stress Urinary Incontinence. J Physiother Res Vol.5 No.10:48
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI) was seen predominantly in women. SUI is seen as common causative factors for females suffering from incontinence over the age of 40-50 years. SUI happens when physical movement or activity such as coughing, laughing, sneezing, running or heavy lifting puts pressure on your bladder causing the patient to leak urine. Kegel exercise and plyometric exercise treats SUI symptoms by reinforcing weakened pelvic floor muscle and improving elasticity.
Objective: To determine the efficacy of Kegel exercises and lower limb plyometric on pelvic floor muscle functions in symptoms associated with SUI
Methodology: This is an interventional study. 20 samples were diagnosed with SUI from urology department, MGMCRI. Aged between 40-50 years, who fulfilled inclusion criteria were selected. Subjects having patients who are suffering from CNS disorder, acute mental illness, Urology surgery, malignancy, urinary infection, hysterectomy, diabetic and degenerative conditions were excluded from the study. Samples were divided into two Groups A and B. Group A samples received Kegel exercise and Group B samples received plyometric exercises for a period of 3 months. Samples were asked to fill the questionnaire before and after exercise program. Pre and Post-test values were documented by using the I-QOL questionnaires.
Result analysis: Data’s are interpreted with the help of Incontinence quality of life questionnaire (schurch).
Conclusion: According to the results Lower limb Plyometric exercise found to be an effective treatment than the Kegel exercise for symptoms associated with SUI.
Keywords
Stress urinary incontinence; Kegel exercise; Plyometric exercise; QUID; I-QOL
Introduction
The prevalence of stress urinary incontinence was seen predominantly in women aged between above 40-50 years in Indian population. Urinary incontinence can be caused due to various reasons out of which stress incontinence is seen as common causative factors for females suffering from incontinence over the age of 40-50 years. Stress urinary incontinence refers to leakage of urine involuntarily when the patient’s sneezes, cough, lifting any heavy weight which puts abnormal pressure on bladder. Stress incontinence is not related to psychological stress.
Stress urinary incontinence has not only become a physical barrier but also a psychological barrier to the women suffering from it. Hence the problem has to be addressed both physically and psychologically.
Though there are various surgical interventions like pubovaginal sling operations and other surgeries, there has not been any single non-invasive modality to intervene in the preventive and curative process of stress urinary incontinence.
The only noninvasive and conservative method that was adopted so far is pelvic floor muscle strengthening exercises in physiotherapy perspective.
The Kegel exercise also known as pelvic floor muscle exercises are once thought to be one of the best exercises to improve the bowl and bladder function. Kegel exercise work by tightening the pelvic floor muscles for period of time, then releasing the pelvic floor. When Kegels are done regularly, it helps to strengthen the pelvic floor which aids in better bladder control and reducing over active bladder symptoms. There are two types of Kegel exercise performed:
i. fast twitch muscle exercise
ii. Slow twitch muscle exercise
The fast twitch exercise is caused a short contraction and it works on the fast twitch muscles and quickly shutoff the flow of urine to prevent leakage. The muscles are quickly tightened, lifted ups and then released.
The second exercise works on the supportive strength of the muscle and is referred to as long contraction. The slow twitch muscle fibers are gradually tightened lifted up and held for several seconds.
Plyometrics are explosive exercise that increases speed, quickness and power. They are exercise in which the muscle exerts a maximum force in short interval of time by moving between muscle extension and muscle contraction using proper biomechanics, to build up strength, improve balance and to bring control.
Plyometrics are highly coordinated and skillful movements requiring high levels of force, it mainly uses the whole body and activates most muscle groups therefore burning more calories in single sessions.
Hence in this study we incorporated some plyometric exercise for lower body to see the effectiveness on symptom associated with stress urinary incontinence.
Material and Methods
This was prospectively planned ancillary analysis of the patients attending the OPD of Urology Department, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute, with symptoms associated with stress urinary incontinence. The patients were then referred to physiotherapy department for Non-Surgical therapies for treatment of Stress Predominant Incontinence. In this interventional study 20 participants aged 40 to 50 years old females were chosen among the patients attending OPD with symptoms of SUI. They were asked to sign the informed consent form and asked to complete the demographic questionnaire i.e. QUID (The Questionnaire for female Urinary Incontinence Diagnosis) was used for choosing the type of incontinence in the elderly females. The samples included for the study were the females aged from 40 to 50 years, Patients whose QUID score was 4 and above, who are well built, whose BMI falls within the normal limits (i.e. 18.5 – 24.9) and who are willing to participate in the study till the completion. The exclusion criteria for the study are the patients who were absent for two or more training session, patients who are suffering from central nervous system disease e.g. Multiple Sclerosis, CVA or Acute mental illness, dementia, recent Urology surgery (less than 6 months), history of Genitourinary malignancy, current urinary infection, hysterectomy diabetic mellitus and musculoskeletal disorder apart from pelvic floor muscle weakness.
The patients were then asked to complete the I-QOL (Incontinence – Quality of Life) Questionnaire forms given to them. All the questionnaires were filled by the patients and are documented. Then they were randomly assigned into two group’s care and control group. Each participant took part in exercise programme for 3 months duration with four session in a week, every session lasting for 30 to 50 minutes with interval in between exercises, which comprises of 48 session to complete the programme.
Each group comprising of 10 samples were given set of exercise programme. One group followed Kegel exercises Programme which consists of following exercises namely,
• Assisted heel drop
• Bridging
• Dead bug
• Bird dog
• Squats
All the above-mentioned exercises were performed for 30 to 50 minutes duration. Every single exercise performed for 5 to 6 minutes with 5 repetitions for each exercise. The patient was given a rest period of 2 to 3 minutes between each exercise.
The other group comprising of 10 members were given Plyometric exercise for lower limbs, which consists of following exercises Programme namely
• Side lying-Straight leg circles
• Side lying – bent knee lift
• Corkscrew
• Lunges
• Butterfly
All the above-mentioned exercises were performed for 30 to 50 minutes duration. Every single exercise performed for 5 to 6 minutes with 5 repetitions for each exercise. The patient was given a rest period of 2 to 3 minutes between each exercise.
All the subjects were given a rest interval of 2 to 3 minutes duration in between each exercise programme. The exercise programme was continued for 3 months duration.
Participants were taught about the anatomy of the pelvic floor muscles and lower urinary tract, physiology and continence mechanisms by the well-trained therapist.
Group exercise was performed in different positions and pelvic floor muscles were contracted and relaxed more frequently with each contraction lasting for 6-8 seconds, 3-4 contractions were then added. The rest period was about 2-3 minutes. Several relaxation techniques including breathing exercises, body awareness, strengthening of abdominal, back and thigh muscles were performed between exercise or each position. Music was played throughout exercise program to encourage participants. The participants were asked to perform the home exercise with more intense contractions.
Finally, the subjects filled the I-QOL questionaries’ before and three months after the intervention.
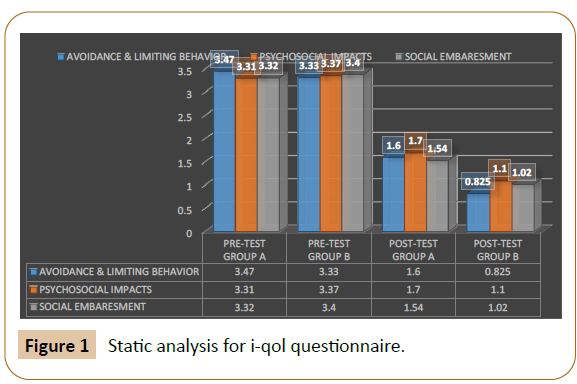
Incontinence quality of life questionnaire consist of three domains i.e., Avoidance and Limiting Behaviour (ALB), Psycho- Social Impacts (PSI) and Social Embarrassment (SE). Avoidance and limiting behaviour domain consist of 8 items (Table 1). Psycho-social impacts domain consists of 9 items (Table 2). Social embarrassment domain consists of 5 items (Table 3 and 4). Totally incontinence quality of life questionnaire consists of 22 items. It was measured by UniPolar Scale proposed by Jon Krosnick, professor of communication at Stanford in 2008 Figures 1-3. Unipolar scale has following ratings from 0 -4 i.e., not at all, slightly, moderately, very moderately & extremely. According to this scale, data was analyzed and documented.
| Do you leak urine (even small drops), wet yourself, or wet your pads or undergarments... | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. When you cough or sneeze? | None of the time |
Rarely | Once in a while | Often | Most of the time |
All of the time |
| 2. When you bend down or lift something up? | ||||||
| 3. When you walk quickly, jog or exercise? | ||||||
| 4. While you are undressing in order to use the toilet? | ||||||
| 5. Do you get such a strong and uncomfortable need to urinate that you leak urine (even small drops) or wet yourself before reaching the toilet? |
||||||
| 6. Do you have to rush to the bathroom because you get a sudden, strong need to urinate? |
Table 1 The Questionnaire for female Urinary Incontinence Diagnosis (QUID).
| Domain | Sl.No | Quality Of Life Questionairre | Unipolar Scale | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| Avoidance And Limiting Behaviour (Alb) | 1 | I worry about not being able to get to the toilet on time | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | I worry about coughing/sneezing because of my incontinence | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 | I have to be careful standing up from sitting | - | - | - | - | ||
| 4 | I worry about where toilets are in new places | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 5 | It’s important for me to make frequent trips to the toilet | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 6 | It’s important to plan every detail in advance because of my incontinence | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 7 | I have difficulty getting a good night’s sleep because of my incontinence | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 8 | I have to watch how much I drink because of my incontinence | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Psychosocial Impacts (Psi) | 1 | I feel depressed because of my incontinence | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | I don’t feel free to leave home for long periods because of my incontinence | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 | I feel frustrated because my incontinence prevents me doing what I want | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 4 | My incontinence is always on my mind | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 5 | My incontinence makes me feel unhealthy | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 6 | My incontinence makes me feel helpless | - | - | - | - | ||
| 7 | I get less enjoyment out of life because of my incontinence | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 8 | My incontinence limits my choice of clothing | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 9 | I worry about having sex because my incontinence | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Social Embarrassment (Se) | 1 | I worry about others smelling urine on me | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | I worry about my incontinence getting worse as I get older | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 | I worry about being embarrassed or humiliated by my incontinence | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 4 | I worry about wetting myself | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 5 | I feel I have no control over my bladder | - | - | - | - | - | |
Table 2 Incontinence Quality of Life (I-QOL) Questionnaire.
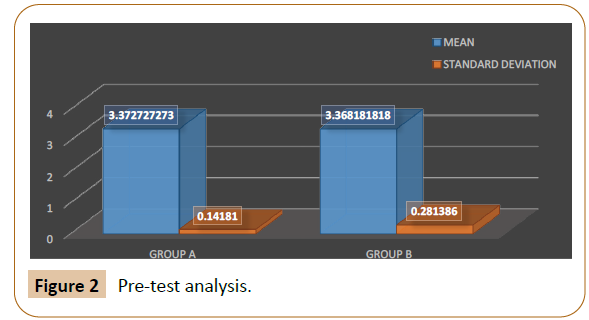
| Group | No. Of Samples | Mean | Standard Deivation | Sem | U -Value | Z Ratio | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10 | 3.372727 | 0.14181 | 0.0204 | 45 | -0.34017 | 0.72786 |
| B | 10 | 3.368182 | 0.281386 |
Table 3 The data were examined using mean and standard deviation and Mann-Whitney U test.
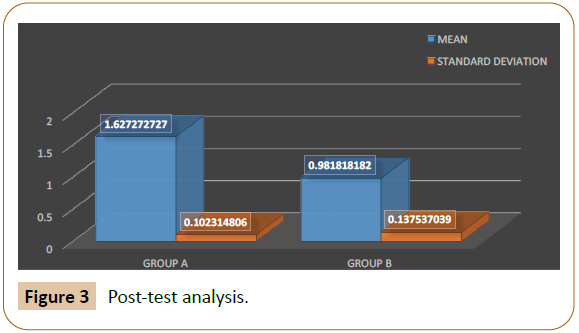
| Group | No. Of Samples | Mean | Standard Deivation | Sem | U-Value | Z-Ratio | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10 | 1.627272727 | 0.102314806 | 0.0163 | 0 | 3.74185 | 0.00018 |
| B | 10 | 0.981818182 | 0.137537039 |
Table 4 By the Conventional criteria, the difference is considered to be statistically significant the Standard Error of Mean=0.0163.
Result and Analysis
The data were examined using mean and standard deviation and Mann-Whitney U test.
Interpretation result:
The data from the above Table 1, Shows the pre-test value of symptoms associated with stress urinary incontinence between tow sample groups (i.e.) Group A & Group B
• The Mean Value & the Standard Deviation of Group A is 3.372727273 & 0.14181 respectively.
• The Mean Value & The Standard Deviation of Group B is 3.368181818 & 0.281386Respectively
• The U-Value between Group A & Group B is 45
• The Z-ratio between Group A & Group B is -0.34017
The P-Value is 0.72786, p <.05 showing the data’s observed consider to be not statistically significant.
The data from the above Table 2, Shows the Post-test value of symptoms associated with stress urinary incontinence between tow sample groups (i.e.) Group A & Group B
• The Mean Value & the Standard Deviation of Group A is 1.627272727 & 0.102314806Respectively.
• The Mean Value & the Standard Deviation of Group B is 0.981818182& 0.137537039Respectively.
• The U-Value between Group A & Group B is 0
• The Z-ratio between Group A & Group B is 3.74185
• The P-Value is 0.00018, i.e. p < .05.
Showing there is a significant difference between the post-test values of Group A & B.
Discussion
In Investigating of urinary incontinence some changes were observed in two groups before and after treatment.
Incontinence has the capacity to affect three major aspects of women’s health, Physical, social and Psychological. Women living with stress urinary incontinence seems to have significantly lower quality of life compared with normal women. The condition has shower to affect areas such as Travel, Sleep, Work, Relationship, Sports and Hobbies.
Since the Kegel exercise was the most popular and a proven form of exercise among women’s suffering from urinary incontinence no other intervention was trained for people with pelvic floor weakness.
The plyometric training was considerably less popular and a more stressful exercise when compared to Kegel exercise. With amount of co-morbidity, obesity associated with weak musculature and sedentary life style made people (women) to go for more convenient and less stressful exercise then sternous exercise.
So, the samples were included and motivated to do move vigorous form of exercise to have the better results.
In a study that was done by [1] discussed the efficacy and safety of lower limb plyometric training in elderly adults concluded that Plyometric training is feasible and safe training option with potential for improving various performance, functional, and health-related outcomes in older persons.
In the study of [2] with title of Lower Body Plyometric Exercise and Pelvic Floor Muscular Engagement concluded that plyometric exercise is more effective in co-recruitment of muscle fibres. The exercise listed above is considered to the most effective pelvic floor engagers from the large number of movements studied. These movements may provide an effective plyometric pelvic floor conditioning program.
In a study that was done by [3], MS concluded that I-QOL is a reliable, valid, and responsive measure of incontinence-related QOL in neurogenic patients.
In the study of [4-18] with the title of The Questionnaire for Urinary Incontinence Diagnosis (QUID): Validity and Responsiveness to Change in Women Undergoing Non-Surgical Therapies for Treatment of Stress Predominant Urinary Incontinence showed that the QUID has acceptable psychometric characteristics and may be used as a UI outcome measure in clinical trials.
Study Limitation
There are number of limitations regarding this study that should be considered when coming to the conclusion of this study:
i. The study population was small involving 10 subjects only on each group
ii. Since the plyometric exercises requires a strenuous workout and very tiring exercise, Persons who are obese and poor muscle strength could not participate the study.
Conclusion
Based on the results obtained from the study it can be concluded that both plyometrics as well .as Kegel exercise had effect on controlling urinary incontinence. There was marginal reduction in all the three domains in the samples who followed Kegel exercise and there was significant reduction in all the three domains in the samples who followed plyometric exercise programmes. The psychological status and the behavioral outcome of the samples clearly shows evidence that plyometrics had better impact then Kegel exercise on urinary incontinence though the sample size is small and the inclusion criteria was very specific, the reason for better outcome with plyometric could be attributed to following reasons. Certain lower body movement seems to induce more effective, co-recruitment of the pelvic floor musculature. Both Kegel exercise and Plyometric exercise have effectively induced co-recruitment of pelvic floor muscles. The exercises listed under plyometrics are considered to be more effective pelvic floor engagers from the results obtained after the study. Poor longterm compliance of Kegel exercises programme illustrates this fact. Better compliance has been found in plyometric exercises programme. It may be the case that plyometric exercises programme for pelvic floor muscles would be better practiced and more effective in restoring and maintaining the pelvic floor fitness.
References
- Tomas V, Michal S, Petr S, James JT (2019) The efficacy and safety of lower limb plyometric training in elderly adults. Sports Med 49(1): 113-131.
- Bruce S, Crawford MD (2008) Lower Body Plyometric Exercise and Pelvic Floor Muscular Engagement.
- Schurch B, de Seze M, Denys P (2005) Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for neurogenic urinary incontinence: results of a single treatment, randomized, placebo controlled 6 month study. J urol 174: 196-200.
- Marzieh KJ, Malihe T, Maryam M (2014) The Effect of Pelvic Muscle Exercises on Urinary Incontinency andSelf-Esteem of Elderly Females With Stress Urinary Incontinency, 2013. Glob J Health Sci 7(2): 71-79.
- McAuley E, Elavssky S, Motl RW, Konopack JF, Hu L, Marquez DX (2005) Physical activity,self-efficacy, and self-esteem: longitudinal relationships in older adults. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci 60(5): 268-275.
- Nygaard I, Barber MD, Burgio KL, Kenton K, Meikle S, Schaffer J, et al. (2008) Prevalence of symptomatic pelvic floor disorders in US women. JAMA 300: 1311-1316.
- Charambous S, Trantafylidis A (2009) Impact of urinary incontinence on quality of life. Peoviperineology 28: 51-53.
- Hong JY (1997) The efficacy of pelvic floor muscle exercise in patients with genuine stress incontinence. Kor J Urol 38(6) 639-643.
- Bradley CS, Rovner ES, Morgan MA, Berlin M, Novi JM, Shea JA, et al. (2005) A new questionnairefor urinary incontinence diagnosis in women: development and testing. Am J Obstet Gynecol 192: 66-73.
- Daneshgari F (2010) Surgical treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, decades learned lessons. Euro Urol 58(2) 239-241.
- Sarl D (2007) The effects of pelvic floor muscle exercise on urinary incontinence and quality of life.
- Swithenbank LV, Abrams P (1999) The impact of urinary incontinence on the quality of life of women. Wld J Urol 17: 225-229.
- Nygaard I, Thom D, Calhoun E (2000) Urinary incontinence in women. In: Litwin MG, Saigal CS editors. Urologic diseases in America. Washington, DC.
- Long RM, Giro SK, Flood HD (2008) Current concepts in female stress urinary incontinence. Surgeon 6(6): 66-372.
- Hewitt J (2001) The complete yoga book. New York: Schocken Books Inc.
- Tenfelde S, Logan R, Abernethy M (2014) Yoga from the pelvic floor. Beginnings (American Holistic Nurses Association). 34(1): 24-26.
- Steers WD (2002) Pathophysiology of overactive bladder and urge urinary incontinence. Reviews in Urology 4: 7-18.
- Sinclair AJ, Ramsay IN (2011) The psychosocial impact of urinary incontinence in women. Obstet Gynecol 13(3): 143-148.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences