Polymer Congress 2018
Polymer Sciences
ISSN: 2471-9935
Page 60
June 04-05, 2018
London, UK
4
th
Edition of International Conference on
Polymer Science and
Technology
Dae Su Kim et al., Polym Sci 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.4172/2471-9935-C2-012
Characterization of composite films prepared by in-situ
polymerization of styrene/butyl acrylate in nanoporous
cellulose gels
Dae Su Kim
and
Jyoti Sankar Borah
Chungbuk National University, Republic of South Korea
P
olymer/cellulose composites have attracted lots of interest
because they can have high strength to weight ratios, low
thermal expansion coefficients, cost competitiveness, and
eco-friendliness. To prepare a high performance polymer/
cellulose composite the chemical modification of cellulose
would be essentially carried out via the hydroxyl groups of
cellulose to make the hydrophilic cellulose more compatible
to the generally hydrophobic polymer. However, manufacturing
a high performance polymer/cellulose composite is still a
challenge because of the poor dispersion and distribution
of cellulose fillers in a hydrophobic polymer matrix and poor
interfacial adhesion between cellulose and the polymer
matrix. Most of the published studies on polymer/cellulose
composites used natural cellulose fillers (fibers or particles)
with native molecular structure. However, nanoporous
cellulose gels (NCGs) with regenerated molecular structure
can be prepared by dissolution and coagulation of native
cellulose molecules and used as fillers to reinforce polymers.
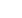
Therefore, in this study, film-shape NCGs were prepared first
using microcrystalline cellulose powder via (1) dissolution
of cellulose chains in an aqueous alkali hydroxide/urea
solution and (2) crosslinking of cellulose chains by adding
epichlorohydrin to (1). Then, poly(styrene-co-butyl acrylate)/
NCG composite films were prepared by in-situ polymerization
of each styrene/butyl acrylate (St/BA=3/7~7/3) monomer
mixture with benzoyl peroxide 1% as an initiator in the NCGs. A
monomer mixture was imbedded in the cavities of an NCG first
then in-situ polymerized at 50°C for 12 h. The NCG contents in
the composite films were controlled from 16 vol.% to 44 vol.%
by controlling the dewatering level of the pristine nanoporous
cellulose hydrogel using different compression forces. The
composite film prepared with St/BA=3/7 monomer mixture
was highly transparent (~82%) in the visible region and showed
excellent tensile and dynamic mechanical properties.
Recent Publications
1. Jang S Y and Kim D S (2016) Physical properties of
polypropylene composites with hydrophobized cellulose
powder by soybean oil. J Appl. Polym. Sci. 133(6):42929.
2. Xu C et al. (2017) Polylactide/cellulose nanocrystal
composites: a. comparative study on cold and melt
crystallization. Cellulose. 24(5):2163-2175.
3. Tanaka S, Iwata T and Iji M (2016) Solvent effects on
heterogeneous synthesis of cardanol- bonded cellulose
thermoplastics. Polymer. 99:307-314.
4. Cai J, Kimura S, Wada M and Kuga S (2009)
Nanoporous cellulose as metal nanoparticles support.
Biomacromolecules. 10(1):87-94.
5. Chang C and Zhang L (2011) Cellulose-based hydrogels:
present status and application prospects. Carbohydrate
Polymers. 84(1):40-53.
Figure 1:
Preparation of NCG and a poly(styrene-co-butyl acrylate)/NCG composite.