Polymer Congress 2018
Polymer Sciences
ISSN: 2471-9935
Page 56
June 04-05, 2018
London, UK
4
th
Edition of International Conference on
Polymer Science and
Technology
Qin Hu, Polym Sci 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.4172/2471-9935-C2-012
Determination of semicarbazide in fish by molecularly
imprinted stir bar sorptive extraction coupled with high
performance liquid chromatography
Qin Hu
Nanjing Medical University, China
A
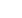
novel molecularly imprinted stir bar (MI-SB) for sorptive
extraction of semicarbazide (SEM) was fabricated in
present paper. The coating of the stir bar was characterized
by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier-transform infrared
spectroscopy, dynamic adsorption and static adsorption tests.
In order to optimize the MI-SB extraction operating conditions
for the analysis of SEM, extraction and desorption solvents
affecting the extraction performance of MI-SB, the extraction
and desorption time of MI-SB for SEM were optimized. Under
the optimized conditions, the saturated adsorption of MI-SB
was about 4 times over that of non-imprinted stir bar (NI-SB).
Urea, DMAC, cysteine andNFZwere used to verify the selectivity
of MI-SB. The recoveries of the MI-SB for SEM kept almost no
changed, and all above 95% when urea, DMAC, cysteine and
NFZ were added into SEM solution. The result showed that
these analogues of SEM did not affect the adsorption of MI-SB
to SEM. The different batches of MI-SBs to adsorb SEM had
no significance difference. Moreover, after three extractions
for a single MI-SB, the recovery of SEM was 86% with RSD of
4.78% (n=3). The results of experiment revealed that the MI-SB
was reproducible and could be used for three times at least. A
method to determine SEM was established by coupling MI-SB
sorptive extraction with HPLC-UV. The liner range was 1-100
ng/mL for SEM with a correlation coefficient of 0.9985. The
limit of detection was about 0.59 ng/mL, which was below the
minimum required performance limit of SEM in meat products
regulated by European Union. The method was applied to the
determination of SEM in fish sample with satisfactory results.
Recent Publications
1. Cooper K.M., Samsonova J.V., Plumpton L., Elliott
C.T., Kennedy D.G. (2007) Enzyme immunoassay for
semicarbazide-The nitrofuran metabolite and food
contaminant, Anal. Chim. Acta 592: 64-71.
2. Gomez-Caballero A., Diaz-Diaz G., Bengoetxea O.,
Quintela A., Unceta N., Goicolea M.A., Barrio R.J. (2016)
Water compatible stir-bar devices imprinted with
underivatised glyphosate for selective sample clean-up,
J. Chromatogr. A 1451: 23-32.
3. Balbão M.S., Bertucci C., Bergamaschi M.M., Queiroz
R.H., MalfaráW.R., Dreossi P.M.L, De S.A., Queiroz M.E.
(2010) Rifampicin determination in plasma by stir
bar-sorptive extraction and liquid chromatography, J.
Pharmaceut. Biomed. 51: 1078-1083.
4. Díaz-Álvarez M., Turiel E., Martín-Esteban A. (2016)
Molecularly imprinted polymer monolith containing
magnetic nanoparticles for the stir-bar sorptive
extraction of triazines from environmental soil samples,
J. Chromatogr. A 1469: 1-7.
5. Ling Z., Xu G., Wei F., Jing Y., Qin H. (2015) Determination
of melamine in powdered milk by molecularly imprinted
stir bar sorptive extraction coupled with HPLC, J. Colloid
Interf. Sci. 454: 8-13.
6. Lei Y., Xu G., Wei F., Yang J., Hu Q. (2014) Preparation
of a stir bar coated with molecularly imprinted polymer
and its application in analysis of dopamine in urine, J.
Pharmaceut. Biomed. 94: 118-124.
Biography
Qin Hu has her expertise in preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers,
nano carbon dots and quantum dots,and their application to the detection
of micro materials in life system.
huqin@njmu.edu.cnFigure 1:
Scheme 1 Schematic representation of the preparation of MIP-SB.