Polymer Congress 2018
Polymer Sciences
ISSN: 2471-9935
Page 57
June 04-05, 2018
London, UK
4
th
Edition of International Conference on
Polymer Science and
Technology
Shuhu Du, Polym Sci 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.4172/2471-9935-C2-012
A single dual emissive nanoprobe for quantification of
spontaneous glucose in human serum
Shuhu Du
Nanjing Medical University, China
I
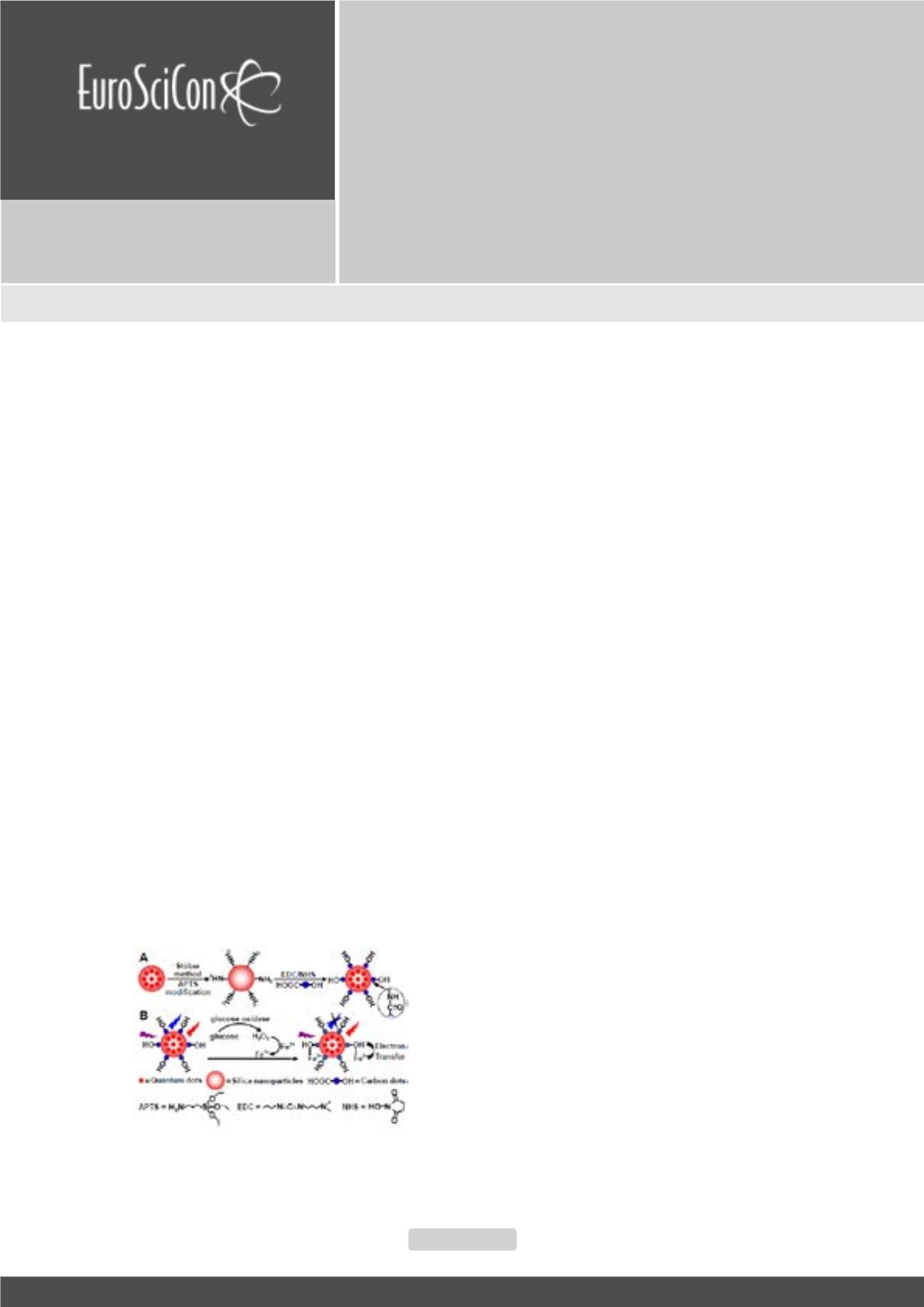
n this work, we report a strategy of a single dual-emissive
ratiometric fluorescent nanoprobe (QDs@SiO2-CDs) with
the controllable ratio of emissive intensities to realize
the consecutive color variations from blue to red for the
quantification of blood glucose. The red quantum dots (rQDs)
were embedded into silica nanoparticles (SiO2 NPs) as an
stable internal standard emission, and blue carbon dots (bCDs)
were further covalently linked onto the surface of SiO2 NPs,
in which the ratiometric fluorescence intensity of blue to red
is controlled at 5: 1(from QDs@SiO2-CDs) was thus quenched
by the electron transfer from CDs to Fe3+. Meanwhile, the
fluorescent intensity (at 630 nm)of rQDs (from Q D s @
SiO2-CDs) keeps almost unchanged. It has been demonstrated
that the fluorescence intensity ratio I445/I630 is linearly related
to the glucose concentration in the range of 0−75 μM (R2 =
0.989). The calculated detection limit is about 3 μM in terms of
the 3σ rule. Consecutive color variations from blue to red with
the dosage of glucose can be seen under a 365 nm UV lamp.
That is to say, the ratiometric fluorescent probe can be
used for the detection of glucose in human serum. The test
result show that the spontaneous blood glucose determined
by the probe wasalmost in accordance with that measured
by a standard glucometer. The method reported here opens a
window to the wide applications of the ratiometric fluorescent
probe in biological assays.
Recent Publications
1. Shaw, J. E.; Sicree, R. A.; Zimmet, P. Z.( 2010) Diabetes
Res. Clin. Pract. 87, 4‐14.
2. Whiting, D. R.; Guariguata, L.; Weil, C.; Shaw, J.( 2011)
Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 94, 311‐321.
3. Han, M.; Gao, X.; Su, J. Z.; Nie, S.( 2001) Nat. Biotechnol.
19, 631‐635.
4. Jiang, W. X.; Dong, X.; Jiang, J.; Yang,Y. H.; Yang, J.; Lu,
Y. B.; Fang, S. H.; Wei, E. Q.; Tang, C.; Zhang, W. P.( 2016)
Sci. Rep. 6, 20568‐20576.
5. Grossi, M.; Morgunova, M.; Cheung, S.; Scholz, D.; Conroy,
E.; Terrile, M.; Panarella, A.; Simpson, J. C.; Gallagher, W.
M.; O’Shea, D. F. (2016) Nat. Commun. 7,10855‐10867.
6. Kamiyama, D.; Sekine, S.; Barsi‐Rhyne, B.; Hu, J.; Chen,
B.; Gilbert, L. A.; Ishikawa, H.; Leonetti, M. D.; Marshall,
W. F.; Weissman, J. S.; Huang, B.( 2016) Nat. Commun.
7, 11046‐11054.
7. Sandanaraj, B. S.; Gremlich, H. U.; Kneuer, R.; Dawson, J.;
Wacha, S.( 2010) Bioconjugate Chem. 21, 93‐101.
8. Zheng, M.; Ruan, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, T.; Qu, D.; Zhao, H.;
Xie, Z.; Gao, H.; Jing, X.; Sun, Z.( 2015) ACS nano 9,
11455‐11461.
Biography
Shuhu Du is working as a professor at Nanjing Medical University, china.
On July, 1987–November, 2004, He was doing as research fellow in Anhui
Academy of Medical Sciences. His work was for the Drug development
research.
shuhudu@njmu.edu.cnScheme 1. Schematic illustration of (A) the synthesis of the
dual-emission ratiometric fluorescent probe QDs@SiO2-
CDs nanoparticles and (B) the visual detection of glucose.