Polymer Congress 2018
Polymer Sciences
ISSN: 2471-9935
Page 58
June 04-05, 2018
London, UK
4
th
Edition of International Conference on
Polymer Science and
Technology
Xuemin Zhou et al., Polym Sci 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.4172/2471-9935-C2-012
DNA-silver nanoclusters molecular beacons as a novel
nanoprobe for sensitive and label-free fluorescent
detection of transcription factors
Xuemin Zhou, Bingzhi Li, Lei Xu, Yue Chen, Wanying Zhu, Xin Shen, Chunhong
Zhu, Jieping Luo, Xiaoxu Li
and
Junli Hong
Nanjing Medical University, China
A
s a fluorescent bio-molecule functionalized nanomaterial,
DNA-silver nanoclusters (DNA-AgNCs) has attracted
substantial research interest. Whereas, the application of
this material is still focused on detecting nucleic acids and
developing aptamer-based sensors, where we believe that the
application scope of DNA-AgNCs can be further expanded.
Transcriptionfactors(TFs)arekeyregulatorsingeneexpression,
and their dysregulation are involved in numerous diseases.
Thus, they are therapeutic targets and potential diagnostic
markers. However, present methods for TFs detection are
either cumbersome or costly. Herein, we firstly applied DNA-
silver nanoclusters molecular beacons (AgMBs) in TFs analysis
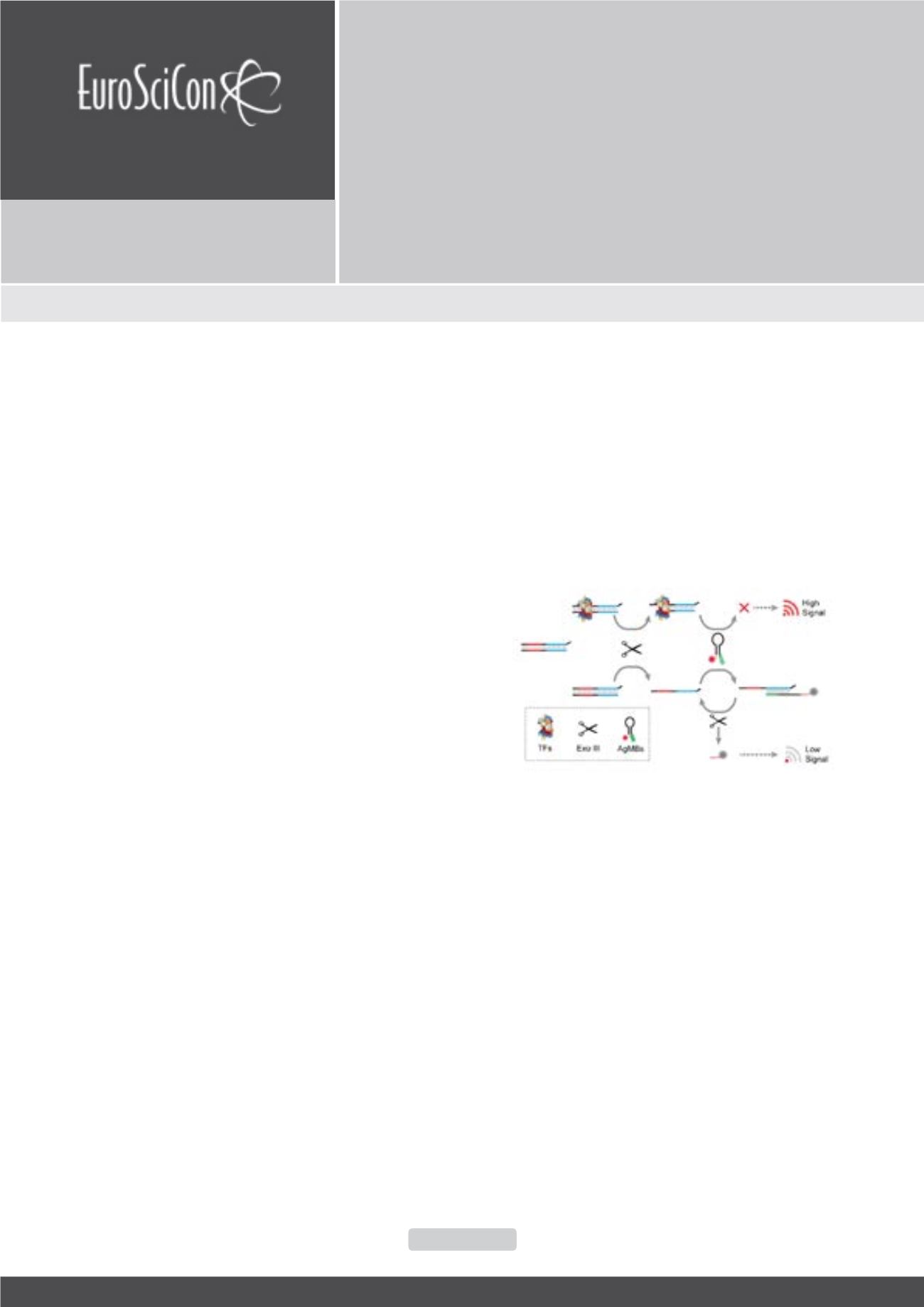
and designed an assay based on the switchable fluorescence
of AgMBs. In the absence of TFs, a single-stranded DNA
functioned as a reporter is released from a double-stranded
DNA probe (referred as dsTFs probe) under exonuclease III
(Exo III) digestion. Then, the reporter triggers downstream Exo
III-assisted signal amplification by continuously consuming
the guanine-rich enhancer sequences in AgMBs, resulting in
significant fluorescent decrease eventually. Conversely, the
presence of TFs protects the dsTFs probe from digestion and
blocks the downstream reaction to keep a highly fluorescent
state. To testify this rationale, we utilized nuclear factor-kappa
B p50 (NF-κB p50) as a model TFs. Owing to the amplification
strategy, this method exhibited high sensitivity towards NF-κB
p50 with a limit of detection of 10 pM, and a broad linear range
from 30 pM to 1.5 nM. Furthermore, this method could detect
multiple TFs in human colon cancer DLD-1 cells and reflect
the variation in their cellular levels after stimulation. Finally, by
conducting an inhibition assay we revealed the potential of this
method for screening TFs-targeted drugs and calculating the
IC50 of corresponding inhibitors.
Recent Publications
1. Xu L et al. (2017) G-quadruplex based Exo III-assisted
signal amplification aptasensor for the colorimetric
detection of adenosine. Anal Chim Acta. 980:58-64.
2. Zhu W et al. (2016) Magnetically controlled
electrochemical sensing membrane based on
multifunctional molecularly imprinted polymers for
detection of insulin. Electrochim Acta. 218:91-100.
3. Han Q et al. (2016) Magnetic sensing film based on
Fe3O4@Au-GSH molecularly imprinted polymers for
the electrochemical detection of estradiol. Biosens
Bioelectron. 79:180-186.
Biography
Xuemin Zhou is a Professor in the School of Pharmacy at Nanjing Medical
University, China. Her current research interests include the design and the
development of separation method, nanomaterials and electrochemical
sensor for the analysis of target molecules in complex matrix.
xueminzhou001_001@hotmail.comFigure 1:
The sensing approach of AgMBs-basedTFs assay.