Anaesthesiology
Anesthesia comes from the Greek meaning sensation loss Anesthetic procedure has grown from a desire for pain relief and altered perception to enable surgery. In addition, a reversible state of unconsciousness is accomplished with anesthesia. It can be divided into three stages: induction, upkeep, and emergence. Nerve transmission is blocked in regional anesthesia, and the patient may remain awake or be sedated or anesthetized during the procedure. Anesthesia of conduction in which small nerves are not anesthetized individually, as in anesthesia of the nerve block, but rather blocked by local anesthetic solution injected to form a barrier close to the operating site. Peripheral blocks of the nerves (PNB) used for surgical anesthesia as well as postoperative and nonoperative analgesia. In some clinical conditions PNBs give distinct advantages over general or neuraxial anesthesia.
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 131
Journal of Surgery and Emergency Medicine received 131 citations as per Google Scholar report
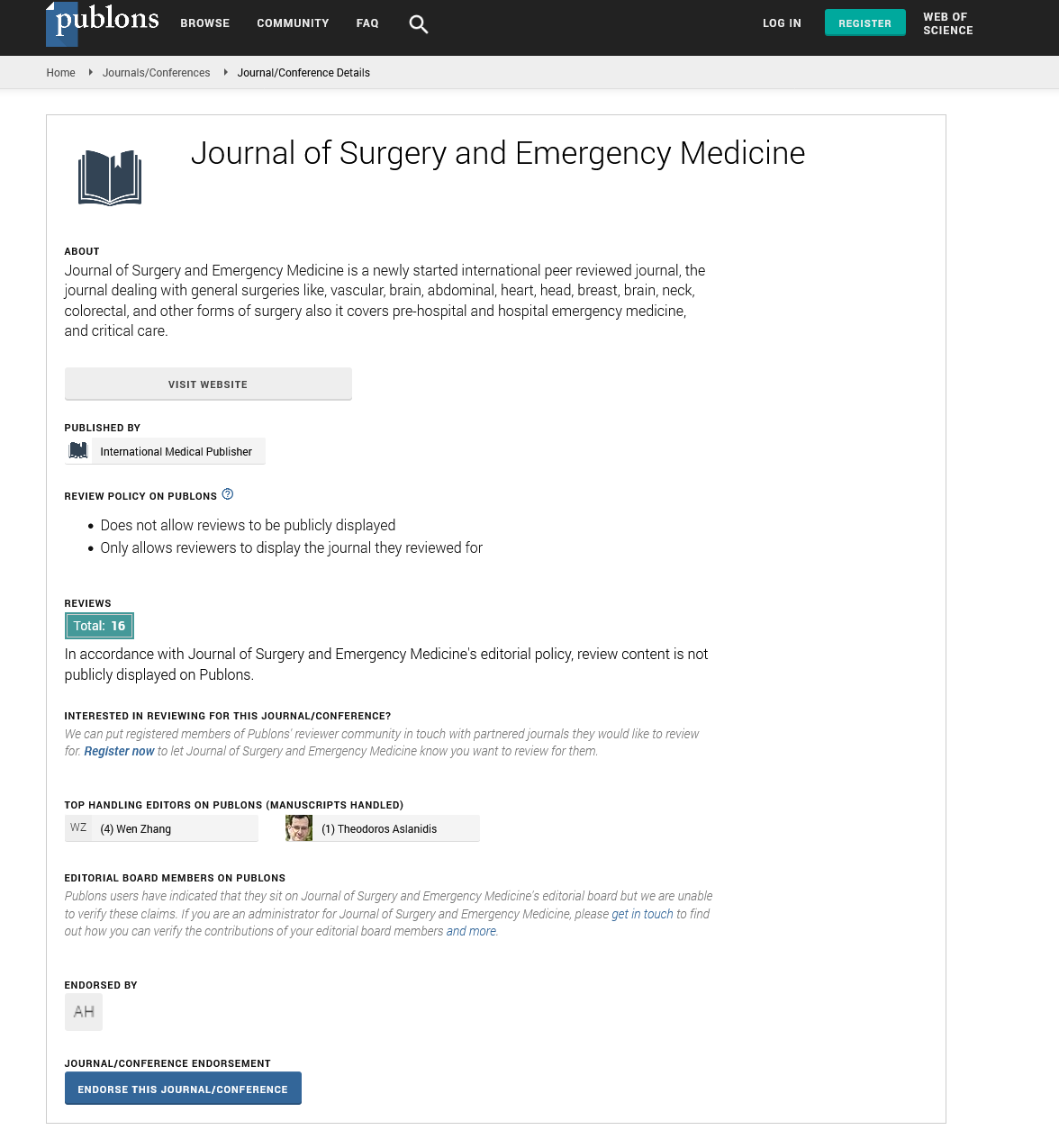
Journal of Surgery and Emergency Medicine peer review process verified at publons
Abstracted/Indexed in
- Google Scholar
- Publons
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences