ISSN : 2321-2748
American Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics
Quality of Different Brands of Metronidazole Available in Jimma Town, South West Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Pharmaceutical Quality Study
1School of Pharmacy, College of Health and Medical Sciences, Haramaya University, Ethiopia
2School of Pharmacy, Institute of Health Sciences, Jimma University, Ethiopia
- *Corresponding Author:
- Teshome Sosengo
School of Pharmacy
College of Health and Medical Sciences
Haramaya University, Ethiopia
Tel: +251973195329
E-mail: teshomesosengo@gmail.com
Received Date: December 24, 2020; Accepted Date: January 05, 2021; Published Date: January 13, 2021
Citation: Sosengo T, Mohammed T, Tatiparthi R (2021) Quality of Different Brands of Metronidazole Available in Jimma Town, South West Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Pharmaceutical Quality Study. Am J Phytomed Clin Ther Vol.9 No.1:2
Abstract
Background: Poor quality medicines include substandard and falsified (i.e., counterfeited) medicines. WHO report of 2017 estimates that the rates of substandard and falsified medical products in low- and middle-income countries is approximately 10.5% with an estimated spend of US$ 30.5 billion.
Objective: The purpose of the study is to assess the quality of different brands of metronidazole available in Jimma town, Oromia region, South West Ethiopia.
Methods: Cross-sectional study was conducted in Jimma town, Oromia regional state, Ethiopia. The study was conducted from May 03 – July 30, 2018. Samples were collected using convenience sampling technique. The samples were analyzed using a methods specified in British Pharmacopoeia 2013 and United States Pharmacopoeia 2015. The assay result of all the seven brands of metronidazole and dissolution test result of the three brands of metronidazole capsules was entered to statistical package for social sciences software version 24.0 for windows. Then, one way analysis of variance was performed using Tukey test to determine whether there exists significant difference in assay and dissolution test results within and among the brands of the respective dosage forms (p<0.05).
Results and Discussion: The quality of brands (three Metronidazole capsules and four Metronidazole injections brands) of Metronidazole was assessed based up on a method specified in BP 2013 and USP 2015. All the seven brands of Metronidazole analyzed for quality passed identity test specification of BP 2013. The three brands of Metronidazole capsules passed weight uniformity and dissolution test specification of USP 2015. The seven brands of Metronidazole passed assay (i.e., drug content) test specification of USP 2015. The highest percentage of drug content, 107.81% and 105.56%, obtained for Metronidazole (generic) (capsule), Nirmet (injection) respectively. However, statistical comparison of assay of respective brands of the respective dosage forms at 95% confidence interval indicates that there exists significant difference in assay within and among the brands of the respective dosage forms (p<0.05). All the four brands of Metronidazole injections passed USP 2015 limit for Endotoxin, Endotoxin limit < 0.35 Eu/ml. Two brands of Metronidazole injection, Aldezol and Metris, failed sterility test from the four brands of Metronidazole injections included in the study and hence of poor quality. The pH of Metronidazole injections were within BP 2013 specification range.
Conclusion: The result of the current study revealed that there was incidence of poor quality Metronidazole in Jimma town. Therefore, post marketing quality assessment should be performed routinely to determine quality status of the drug on market.
Keywords
Counterfeit drugs; Falsified drugs; Poor quality drugs; Quality; Substandard drugs
Introduction
Poor quality medicines include substandard and falsified (i.e., counterfeited) medicines. Substandard medical products are authorized medical products that fail to meet either their quality standards or their specifications or both. Poor quality drugs are worldwide problem with high prevalence in low and middle income countries. WHO report of 2017 estimates that the rates of substandard and falsified medical products in low- and middleincome countries is approximately 10.5% with an estimated spend of US$ 30.5 billion [1,2].
WHO global surveillance and monitoring system for substandard and falsified medicines has received more than 1500 reports of substandard or falsified medicines, with 42% of reports coming from sub-Saharan Africa, and 21% each coming from the Americas and Europe in the years from 2013-2017. During the years, 8% of reports came from the Western Pacific, 6% from the Eastern Mediterranean and 2% from South-East Asia [1]. The problem of poor quality medicines affects almost all categories of drugs [3]. Antibiotics and anti-malarias are most commonly reported poor quality drugs [4]. Systematic literature review of substandard and counterfeit medicines performed on 15 studies report out that 28.5% of the samples included in the studies were of poor quality. In the study, antibiotics being the most commonly reported poor quality drugs followed by anti-malarial drugs [3].
Poor quality pharmaceuticals frequently fail to meet critical quality attributes specification limit set for them when tested for quality. Failure to comply with API, dissolution and disintegration specification is most commonly reported problems in poor quality pharmaceuticals [5,6]. A retrospective quality assessment study done in Canada on 653 defective drugs report out that 205 (32%) of the products have low concentrations of active ingredients, impurities, dissolution and disintegration failures [2]. In August 2013, Ghana seized 64 000 doses of falsified antimalaria medicines that when tested found to contain only 2% of API [1].
In Sub-Saharan Africa an estimated 400,000 children are exposed to malaria are treated with poor quality anti-malaria medicines [7]. Treatment of patients with poor quality pharmaceuticals causes deleterious problems as treatment failure, increased morbidity and mortality, wastage of budget of family and government and emergence of drug resistance [8-11].
Metronidazole is [1- (2 hydroxyethyl)-2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole] BCS class I drug that was discovered in the 1960s. Since from its discovery, it is used in treatment of numerous infections caused by bacteroides, clostridia, helicobacter, trichomonas, giardia and entamoeba, dental infections, skin infections, surgical prophylaxis and antibiotic associated pseudomembraneous colitis [12-14]. The chemical structure is shown below in Figures 1-4. In spite of its broad use, poor quality Metronidazole has been frequently reported [15,16]. A systematic literature review done in Japan on 86 studies found out that metronidazole was the second most repeatedly reported substandard antibiotic next to cloxacillin and from the 277 samples of metronidazole included in the literature review, 69 (24.9%) of the metronidazole samples were sub-standard [17]. Treatment with substandard dose of metronidazole causes emergence of drug resistance and treatment failure [18,19].
In Ethiopia, except a few attempt of certain scholars to assess quality of certain drugs circulating on the pharmaceutical market of the country, the quality status of majority of the drugs circulating in the health care system of the country yet remain unknown. Therefore, this study assessed the quality of different brands of metronidazole marketed in Jimma town.
Materials and Methods
Study area and period
The study was conducted in Jimma town, Oromia regional state, Ethiopia. It is located 352 km South West of Addis Ababa. Currently in Jimma town there exits 33 drug stores and 22 pharmacies serving the population. The study was conducted from May 03 - July 30, 2018.
Study design
A cross sectional study was conducted to determine quality of Metronidazole available in Jimma town.
Sample collection technique
Samples were collected using convenience sampling technique [20]. Detailed information of the samples purchased for analysis of quality on the present study is indicated in Tables 1 and 2.
| Â Manufacturer | Brand name | Strength | Batch No | Mfg. date | Exp. date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPHARM. Ltd., Ethiopia | Metronidazole (Generic) |
250 mg | BN712018 | 07/2017 | 12/2021 |
| Cadilla Pharmaceuticals Plc, India | Camezol | 250 mg | D17062bx56 | 12/2017 | 11/2020 |
| Addis Pharmaceuticals Factory Plc, Ethiopia |
Metazol           | 250 mg | BN23336 | - | 06/21 |
Table 1: Detailed information on Metronidazole 250 mg capsule analyzed for quality.
| Manufacturer | Brand Name | Strength | Batch No | Mfg. date | Exp. date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aculife Health care Pvt.Ltd., India | Nirmet | 500 mg/100 ml | 2H61981 | Aug, 2016 | Jul, 2019 |
| Unique Pharmaceuticals Labs., India | Metrogyl | 500 mg/100 ml | Plx7070 | April 2017 | March 2020 |
| Albert David Ltd., India | Aldezol | 500 mg/100 ml | P6130023E | June 2016 | May 2019 |
| Claris Otsuka Pvt., India | Metris | 500 mg/100 ml | C262629 | October 2016 | August 2019 |
Table 2: Detailed information on metronidazole injections analyzed for quality.
Quality assurance
Sample collectors (i.e., mystery shoppers) were trained for 1 day. The training was given on allocation of pharmacies and drug stores for sample collection and how to purchase enough samples to allow for quality assessment [20]. Then, the samples were brought to Ethiopian pharmaceutical manufacturing company (EPHARM) quality control laboratory next day to the day of completion of sample collection for analysis. To ensure reliability of results, calibrated and validated equipments was used for all procedures and relevant standard operating procedures (SOPs) was followed for all tests during the laboratory analysis of the samples.
Data analysis
The assay result of all the seven brands of metronidazole and dissolution test result of the three brands of metronidazole capsules was entered to statistical package for social sciences software version 24.0 for windows. Then, one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using Tukey test to determine whether there exists significant difference in assay and dissolution test results within and among the brands of the respective dosage forms (p<0.05).
Ethical approval
The study was reviewed and approved by the ethical review committee of Jimma University, Institute of Health.
Operational definitions
Assay: Content of active pharmaceutical ingredient.
Biopharmaceutical classification system I (BCSI) drugs: Drugs that have high permeability and high solubility and rate limiting step for absorption to systemic circulation is dissolution of the drug.
Contamination: The undesired introduction microbes to a pharmaceutical dosage form above tolerance limit tolerable in official compendias.
Identity: Presence of specified active ingredient.
Poor quality: Drugs that fail to meet quality specification set for them.
Specification: Set of criteria to which a drug product should conform to be considered acceptable for its intended use.
Stability of medicines: The ability of the medicines to maintain the physical, chemical, and microbial properties during the time of storage and usage by the patient.
Equipments
FTIR 8400S (SHIMADZU, Japan), HPLC (Japan), dissolution tester (India), UV-Spectrophotometer (Shmadzu/Japan), evaporating dish (Britain), sonicator (Bandelin/Germany), thermometer (Frankfurt/Germany), volumetric flask (England), pycnometer (Germany), Whatman GFC paper (England), conical flask (MERK / Germany), 0.45 μm Nylon membrane filter (Germany), analytical balance (METLER TOLEDO, Switzerland), pH (Metler Toledo, China), incubator (SANYO, Japan), heating oven (Eclipse, Italy), and KBr (Britain).
Solvents/Chemicals/Reagents
Methanol (CARLOERBA/France), 1 M phosphoric acid (Germany), 0.1 N HCl (Schlau/Spain), Nacl (Fischer scientific/UK), monobasic potassium phosphate (CARLOERBA/France), thioglycolate medium (Himedia laboratory Pvt. Ltd/India), Isopropyl alcohol (National Alcohol/Ethiopia),acetone (CARLOERBA/France), LAL reagent (Charles River/India), TSA (Sisco reasercher Laboratory/ India), Water for bacterial endotoxin test (Nearlite/India), Endotoxin reagent (Charles reagent/India),distilledwater (EPHARM/Ethiopia).
Metronidazole ICRS (Lot number: 183118, WHO center for chemical reference substances, Sweden) was obtained from EPHARM.
Tests
Identification tests: Identification Test of Metronidazole Capsules: Metronidazole capsules identification test was carried out according to a method specified in British Pharmacopoeia (BP) 2013. First, the content of 10 capsules was mixed. Then, 10 mg of Metronidazole sample was taken in potassium Bromide plate ( KBr) plate to the fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) instrument for the identification test (BP, 2013).
Identification Test of Metronidazole Injections: Identification test for Metronidazole injections was done based on BP 2013. First, 20 ml of Metronidazole injection and 9g NaCl was collected in separatory funnel and shacked for 5 minutes [20]. Then, 20 ml of acetone was added to it and the mixture was allowed to separate. The upper layer was evaporated to dryness in an evaporating dish and 10 mg of the sample was taken in KBr plate to FTIR instrument for the identification test.
Weight uniformity test: Weight uniformity test was as per a method specified in United States Pharmacopeia . First, 10 capsules were selected randomly. Then, each intact capsule was weighed and its shell was opened and its content removed. The empty shell was weighed and the net weight of the content of the each capsule was determined by subtracting the weight of the shells from the weight of the intact capsule. The procedure was repeated for the remaining 9 capsules.
Dissolution test: Dissolution test for Metronidazole capsules was performed using a USP Apparatus I. The paddle was set at 100 rpm and 900 ml dissolution 0.1N HCl was used to test all samples. Prior to dissolution testing, the dissolution media was preheated and degassed. Dissolution testing was started after the temperature of 37°C ± 0.5 ºC was confirmed in all six vessels. In pre-set time points of 10, 15, 20, 30, 45 and 60 minutes, 5 ml of the sample solution was taken with syringe from the dissolution vessel and filtered through 0.45 μm membrane filter. Then, the first 2ml was discarded and the remaining 3 ml of the filtrate was transferred to 50 ml volumetric flask and diluted to a volume with 0.1 N HCl . Then, 1.5 ml the sample solution was placed in Quartz cuvets and put in to UV spectrophotometer and its reading was recorded.
Assay tests
Assay test for Metronidazole capsules: Assay test was done using a method specified in USP 2015 (22).
Assay test for Metronidazole injections: Assay test was done using a method specified in USP 2015 (22).
Microbiological tests
Endotoxin test: Endotoxin test was done according to a method specified in USP 2015. The sample solution was prepared by mixing 0.1 ml of the sample stock solution and 0.1 ml of LAL solution and stored at 37°C for 1 hour.
Sterility test: Sterility test was done based on a method indicated on USP 2015. The exterior of all product primary containers was cleansed with 70% isopropyl alcohol and allowed to completely dry. Then, the samples were taken to the working area and all the contents of the bottles were aseptically filtered through a two 0.45 μm membrane filters. The filters was rinsed with five 10 ml of distilled water. Finally, to each membrane filter, each 100 ml of tryptone soya broth and thioglycolate medium was transferred and incubated for 14 days at 22°C and 32°C respectively.
Results and Discussion
Identification test result
The identification test for all the seven brands was performed according to a method indicated in BP 2013 for identification of the drug. The IR spectrums of the standard (i.e., Metronidazole ICRS) and the samples are coinciding, indicating the standard and the seven brands of Metronidazole analyzed on the present study have similar IR spectrum absorption frequency, which in turn shows identity of API of interest in the samples (Figures 1 and 2). Accordingly, all the brands passed the test for identification test. Identification tests performed on Metronidazole in various countries demonstrate mixed results. As in the present study, all the brands analyzed passed an identity test in a study done at Addis Ababa, Ethiopia and Zaria, Nigeria. In contrary to this study finding, in a study done in Nigeria on 581 drugs, in which the 36 of the samples are Metronidazole tablets and 5 of samples are Metronidazole suspensions, all the Metronidazole suspensions included in the study failed identification test [15-20]. A possible reason that the samples failed an identity test may be the samples of Metronidazole suspensions analyzed on the study were falsified (counterfeited). Treatment with medicines void of active ingredient by failing to suppress infection, leads to build up of pathogens, progression of underlying disease and engenders the development of drug resistance.
Weight uniformity test result
Weight uniformity test was done using a method specified in USP 2015. According to USP 2015 specification, the requirements for dosage uniformity are met if the acceptance value (AV) of the first 10 dosage units is less than or equal to L1%, which 15. Weight uniformity test result of Metronidazole capsule brands is shown in Table 3. Thus, according to the results, all the three brands of Metronidazole capsules passed a weight uniformity test.
| Brand Name | AV. XI (%) | SD | % RSD | M (%) | Acceptance value | USP 2015 limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metronidazole (Generic) | 107.55 | 1.32 | 1.23 | 101.5 | 9.218 | L1<15 |
| Camezol | 102.71 | 2.63 | 2.56 | 101.5 | 7.522 | L1<15 |
| Metazol | 104.04 | 2.2 | 2.12 | 101.5 | 7.82 | L1<15 |
Table 3: Weight uniformity test result of randomly selected Metronidazole capsules (n=10).
Dissolution test result
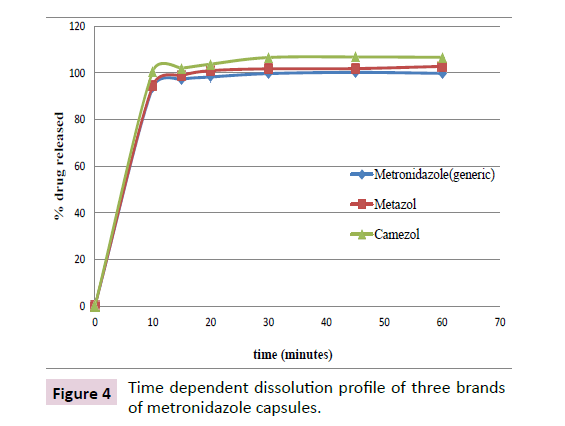
The dissolution test for the Metronidazole capsules was performed using a method specified in USP 2015, in which it is indicated that the 85% of the active ingredient should be released in 30 minutes. In the current study, all the three brands of Metronidazole capsules studied released more than 85% of API within 30 minutes. Statistical comparison of dissolution (release of API) at 95% confidence interval revealed that there exists significant difference in drug release within and among the three brands of Metronidazole capsules (p<0.05). The percentage of dissolution of the brands is shown below (Table 4).
| Variables | % drug released (mean ± RSD; n=6) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Metronidazole (generic) | Metazol | Camezol | |
| 10 | 93.68 ± 2.25 | 94.55 ± 2.55 | 100.67 ± 1.11 |
| 15 | 97.23 ± 1.04 | 98.47 ± 1.3 | 102.04 ± 1.18 |
| 20 | 98.26 ± 1.19 | 100.96 ± 0.97 | 103.76 ± 1.16 |
| 30 | 99.71 ± 1.19 | 101.76 ± 1 | 106.61 ± 1.16 |
| 45 | 100.1 ± 1.507 | 101.86 ± 0.64 | 106.86 ± 1.4 |
| 60 | 99.81 ± 0.788 | 102.80 ± 1.41 | 106.69 ± 1.51 |
Table 4: Result of time dependent dissolution of three brands of Metronidazole capsules (n=6).
Assay test result
For drugs to be therapeutically effective, the formulation ought to contain the API in officially approved extent that produces desired therapeutic effect. All the seven brands of Metronidazole studied passed USP 2015 specification for assay of the product (Table 5). Statistical comparison of drug contents at 95% confidence interval indicates that there exists significant difference in drug content within and among the all the seven brands of Metronidazole (p<0.05). In discrepancy with this study result, failure to comply with assay specification limit was reported in similar in-vitro quality assessment studies conducted on the drug in Eastern Nigeria [16], Myanmar, Bangladesh and China where 3 from 10 brands of Metronidazole tablets, 1 from 14 Metronidazole tablets, 6 from 40 brands of Metronidazole and 41 from 108 Metronidazole failed assay test in the respective studies. The cause for the products to fail assay test on the studies may be the drugs analyzed on respective studies are counterfeited. Substandard quality Metronidazole induces drug resistance, which in turn causes deleterious negative impacts such as increased morbidity, mortality, treatment cost, hospital stay days and others.
| Product | Brand Name | Assay result (%) | ± RSD (%) | USP 2015 limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metronidazole Capsule | Metronidazole (Generic) | 107.81 | 0.113 | 90-110% |
| Camezol | 102.96 | 0.229 | 90-110% | |
| Metazol | 104.34 | 0.138 | 90-110% | |
| Metronidazole Injection | Aldezol | 96.98 | 0.018 | 90-110% |
| Metrogyl | 99.63 | 0.003 | 90-110% | |
| Metris | 100.3 | 0.021 | 90-110% | |
| Nirmet | 101.03 | 0.009 | 90-110% |
Table 5: Assay result of Metronidazole capsules and Metronidazole injections (n=3).
Microbiological quality tests of Metronidazole Injections
Sterility test results: Sterility test result of the samples is indicated in Table 6. The samples were analyzed for sterility as per a method indicated in USP 2015. Two brands (i.e., Aldezol and Metris), failed sterility test from the four brands of Metronidazole injections included in the study and hence of poor quality. Microbiological quality of the liquid dosage forms should be maintained in official specifications limit throughout the shelf life of the drug for the dosage form to be stable and therapeutically effective.
| Product name | Days | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |
| Aldezol | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | +ve | +ve | +ve | +ve | +ve | +ve | +ve | +ve |
| Metris | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | +ve | +ve | +ve | +ve | +ve |
| Metrogyl | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve |
| Nirmet | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve | -ve |
Table 6: Sterility test result of Metronidazole injections (n=1).
Microbial contamination liquid dosage preparations cause spoilage of the product which results in degradation and instability of the product. Subsequent treatment of patients who are already immune-compromised with such microbiologically contaminated products causes increased morbidity and mortality.
LAL test result: The products were tested for bacterial Endotoxin test according to a method specified in USP 2015. LAL test result of Metronidazole injections is shown in Table 7. As indicated on the table, all the four brands of Metronidazole injections passed a test for Endotoxin.
| Brand name | Endotoxin concentration | USP 2015 limit |
|---|---|---|
| Aldezol | <0.25 Eu/ml | <0.35 Eu/ml |
| Metris | <0.25 Eu/ml | <0.35 Eu/ml |
| Metrogyl | <0.25 Eu/ml | <0.35 Eu/ml |
| Nirmet | <0.25 Eu/ml | <0.35 Eu/ml |
Table 7: LAL test result of Metronidazole injections (n=1).
Conclusion
The result of the current study revealed that there was incidence of poor quality Metronidazole in Jimma town. Therefore, post marketing quality assessment should be performed routinely to determine quality status of the drug on market.
Limitation of the Study
Since this study is based upon convenience sampling, the result of the study may not indicate exact quality status of the drug in the study area.
Acknowledgement
The author acknowledges Jimma University School of Pharmacy and Ethiopian pharmaceuticals manufacturing company (EPHARM) for permitting to use their laboratory and freely giving metronidazole standard.
Author’s Contributions
Author Teshome Sosengo involved in the conception and design of the study, participated in the literature searches, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. All the authors approved the final manuscript.
Author Tesfaye Mohammed involved in the conception and design of the study, participated in the literature searches, supervised data collection and analyzed data.
Author Rammanjireddy Tatiparthi participated in the design of the study, supervised data collection and the overall research, and commented the manuscript.
References
- WHO (2017) Who global surveillance and monitoring system for substandard and falsified medical products, Geneva, Switzerland.
- Almuzaini, T Choonara, I Sammons H (2013) Substandard and counterfeit medicines: A systematic review of the literature. BMJ Case Reports 3: e002923.
- Kelesides T, Kelesides I, Rafailidis I, Falagas ME (2007) Counterfeit or substandard antimicrobial drugs: A review of scientific evidence. J Antimicrob Chemother 60: 214-236.
- Kelesidis T, Falagas E (2015) Substandard/counterfeit antimicrobial drugs. Clin Microbiol Rev 28: 443-464.
- Alghannam AFA, Aslanpour Z, Evans S, Schifano F (2014) A systematic review of counterfeit and substandard medicines in field quality surveys. Int J Curr Pharm Res 3: 71-88.
- Sammons HM, Choonara I (2017) Substandard medicines: a greater problem than counterfeit medicines? BMJ Paediatrics Open 1: e000007.
- Seither A (2009) Health and economic consequences of poor quality medicines. Clin Pharm 4: 476-478.
- Newton PN, Green MD, Fernandez FN (2009) Impact of poor-quality medicines in the developing’ world. Pharmacol Sci 31: 99-101.
- Alhedethe P, Alhudaithy K, Zloh M ( 2017) An evaluation of prevalence of low quality of medicines in Saudi Arabia and factors associated an analytical comparative study. Archives in Chemical Research 2: 11–18.
- Wilson JM (2011) The health and economic effects of counterfeit pharmaceuticals in Africa. 2: 1.
- Rediguieri CF, Porta V, Nunes G, Diana S, Nunes S, et al. (2011) Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Metronidazole J Pharm Sci 100: 1618-1627.
- Hedge DD, Strain JD, Heins JR, Farver DK (2008) New advances in the treatment of clostridium diffi cile infection (CDI). Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management 4: 949–964.
- Peedikayil FC (2016) Antibiotics in odontogenic Infections - An update. J Antimicro 2 1–4.
- Dhand A, Snydman DR (2014) Mechanism of resistance in metronidazole mechanism of resistance in metronidazole.
- Taylor R, Shakoor B, Behren O, Everard RH, Low M, et al. (2001) J Pharmacopoeial quality of drugs supplied by Nigerian pharmacies. Lancet 357: 1933–1936.
- Ibezim EC, Attama A, Obitte A, Onyishi NC, Brown VI (2008) In vitro prediction of in vivo bioavailability and bioequivalence of brands of metronidazole tablets in Eastern Nigerian drug market. Sci Res 3: 552-558.
- Tschida S (2016) A systematic review on antibiotic quality. Master of Phlosophy Thesis, Department of Community Health, Oslo University, Norway. p. 18.
- Rasoloson D, Vanacova S, Tomkova E, Razga I, Hrdy P, et al. (2002) Mechanisms of in vitro development of resistance to metronidazole in Trichomonas vaginalis. Microbiology 148: 2467–2477.
- Vander Wouden EJ, Van Zwet AA, Thijs JC, Vosmaer GDC, Oom JAJ, et al. (1997) Rapid increase in the prevalence of helicobacter pylori in the Netherlands. Emerging Infectious Diseases 3 (3): 386-387.
- WHO (2015) Guidelines on the conduct of surveys of the quality of medicines, Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.

Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences