Volume 3, Issue 2 (Suppl)
Trends in Green chem
ISSN: 2471-9889
Environmental & Green Chemistry 2017
July 24-26, 2017
Page 66
5
th
International Conference on
6
th
International Conference on
July 24-26, 2017 Rome, Italy
Environmental Chemistry and Engineering
Green Chemistry and Technology
&
Asymmetric synthesis of potential biologically active new heterocyclic analogs of (S)-
α
-alanine containing
3,4-substituted 5-thioxo-1,2,4- triazoles in the side-chain radical
Hayarpi M Simonyan
1,2
, Lusine Yu Sahakyan
1,2
, Anna F Mkrtchyan
1,2
, Satenik Gh Petrosyan
1,2
, Narine N Baghyan
3
, Ani O Voskanyan
3
, Jaklina N Saribekyan
3
and
Ashot S Saghyan
1,2
1
Yerevan State University, Armenia
2
Scientific and Production Center “Armbiotechnology”, NAS, Armenia
3
“Artsakh Scientific Center” SNPO, Armenia
Statement of the Problem:
Non-proteinogenic α-amino acids are constituents of many physiologically active peptides, antibiotics
and other pharmaceutical preparations. Especially α-amino acids and peptides, containing a N-heterocyclic substituent in the side
chain, are of considerable importance in medicinal chemistry because they combine the pharmacophoric groups of amino acids and
N-heterocycles. These compounds also belong furyl-, thiophenyl- and triazole-containing structures that are important constituents
of many biologically and pharmacologically active drugs such as anti-hyperglycemic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial,
anticancer, antifungal, antitumoral, antiviral and psychotropic.
Aim:
The goal of our research work is elaboration of efficient high-selectivity method for asymmetric synthesis of enantiomerically
enriched substituted α-alanine containing triazole rings in side chain radical.
Materials & Methods:
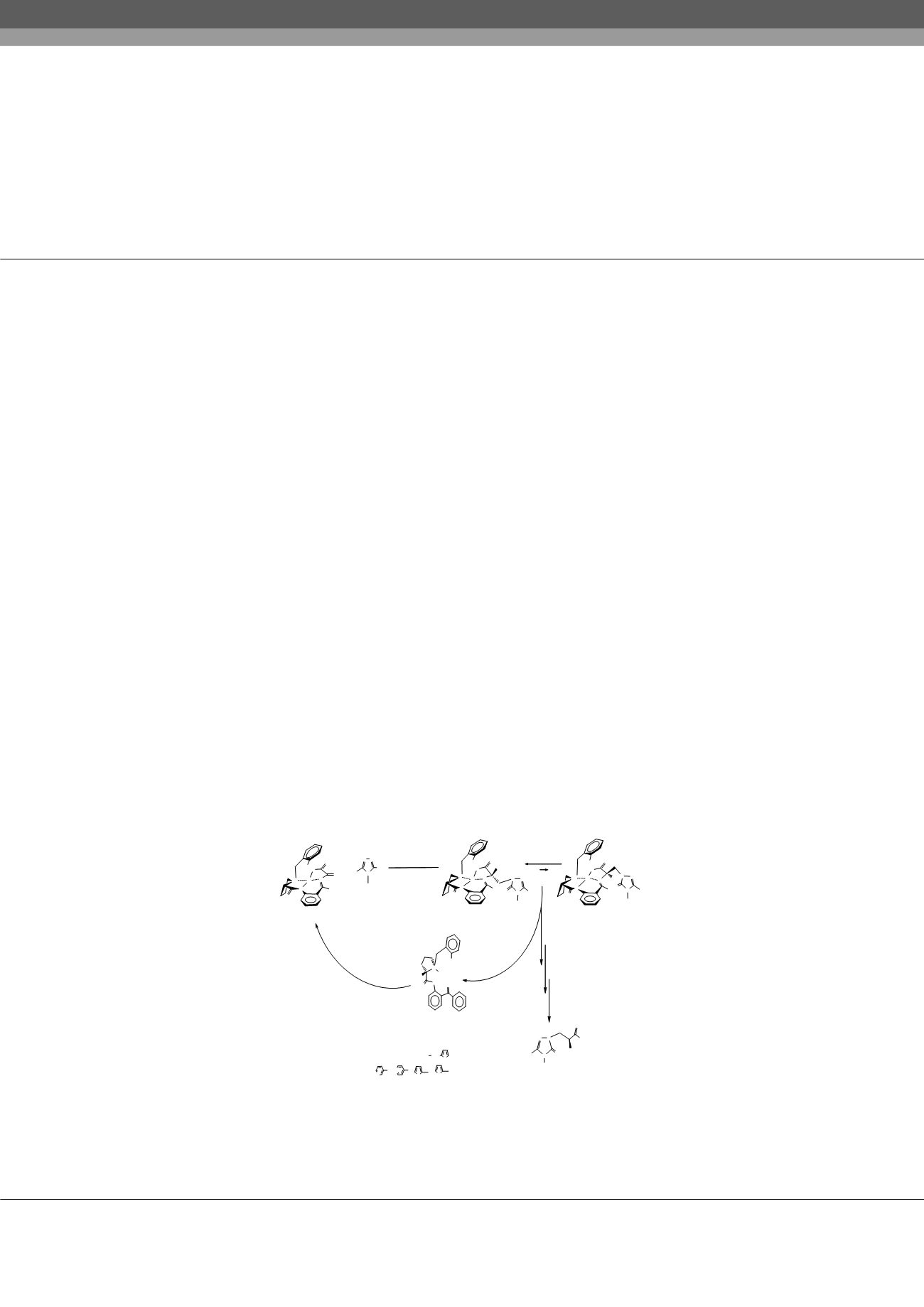
Efficient high-selectivity method for asymmetric synthesis of new heterocyclic substituted derivatives
of α-alanine, through the nucleophilic addition of the substituted triazoles to the C=C bond of dehydroalanine moiety in Nill
complexes of Shiff ’s base with chiral auxiliaries (S)-2-N-(N'-benzylprolyl)aminobenzophenone and (S)-2-N-(N'-chlorbenzylprolyl)
aminobenzophenone was elaborated.
Results:
The results show, that the stereoselectivity of the reaction of nucleophilic addition in case of the complex containing Cl-atom
at the 2nd position of Ph-group of N-benzyl proline moiety is increased (up to 96%). Heterocyclic substituted derivatives of (S)-α-
alanine were isolated with high optical purity (ee>99%) after decomposition of the mixture of the diastereomeric complexes and
ion-exchange purification of the target amino acids.
Conclusion:
The advantage of these complexes is the regenerability of the initial chiral auxiliary reagents in quantitative chemical
yield and complete retention of the original chirality (optical activity) after completion of the synthesis and isolation of the desired
products. This allows multiple reuses of the chiral auxiliaries.
Biography
Hayarpi M Simonyan works in Institute of Pharmacy of Yerevan State University. Her research field of interest is Biomimetic Asymmetric Synthesis. She has her
expertise in elaboration of high selective methods of asymmetric synthesis of enantiomerically enriched non proteinogenic amino acids. She completed her PhD
degree in Chemistry during the year 2013 specializing in Bioorganic Chemistry.
simonyanhayarpi98@gmail.comHayarpi M Simonyan et al., Trends in Green chem, 3:2
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9889-C1-002
Ni
N
O
N
N
Ph
O
O
CH
2
X =
H ,
Ni
II
-
(
S
)
- BPB -
∆
- Ala
X =
Cl ,
Ni
II
-
(
S
)
- 2 - CBPB -
∆
- Ala
+
CH
3
CN
/K
2
CO
3
T = 40 - 50
0
C
O
N
Ni
N
Ph
N
(
S , R
)
(
S , S
)
O
N
N
Ph
O
O
Ni
H
N
N
R
1
N
N S
R
2
N
N
N
SH
R
2
N
R
1
N
N
S
R
2
O
O
H
X
X
X
( s )
N
+
H
O NH O
X
H
Cl
-
6NHCl
40 - 50
0
C
(
S
)
-
BPB
x
HCl
(
S
)
-
2
-
CBPB
x
HCl
Ky - 2x8 , H
+
C
2
H
5
OH
/H
2
O
(1/1)
NH
2
O
OH
NN
S
R
2
N R
1
R
1
R
1
=
C
6
H
5
,
C
6
H
5
(CH
2
)
2
,
CH
2
= C(CH
3
)
-
CH
2
,
CH
3
(CH
2
)
2
,
CH
2
= CH
-
CH
2
,
R
2
= o -
NO
2
C
6
H
4
,
CH
3
(CH
2
)
3
,
(
CH
3
)
2
CHCH
2
,
N
N
O S
O H
2
C
,
,
,
de =
80 - 85%
in case
BPB
de =
90 - 96%
in case
2 - CBPB