Infectious Diseases 2018
Journal of Prevention and Infection Control
ISSN: 2471-9668
Page 43
June 07-08, 2018
London, UK
8
th
Edition of International Conference on
Infectious Diseases
T
oxoplasma gondii
is widely prevalent in most warm-blooded
animals worldwide.
Toxoplasma gondii
is an important zoonotic
and opportunistic parasite especially in the immunocompromised
hosts that can cause significant morbidity and mortality. Humans
mainly get infected by eating undercooked or rawmeat of livestock
as well as contaminated food and drink water. Since cattle play
an important role in the human food chain in Iran, this study was
designed to investigate the infection of slaughtered cattle with
Toxoplasma gondii
in Jahrom, Southern Iran. Briefly, a total of 375
tissue samples consisting of heart, diaphragm, and tongue were
collected from 125 slaughtered cattle in Jahrom abattoir located in
Fars province from June to August 2017.
Toxoplasma gondii
DNA
was extracted from 1 g of the homogenized tissues. A nested-PCR
assay was performed to detect
Toxoplasma gondii
using the SAG2
gene as a target. The total prevalence of toxoplasma infection
among cattle was found to be 96%. The highest infected tissue was
diaphragm (84%) followed by heart (70.4%) and tongue (65.6%).
Co infection of diaphragm, heart and tongue was detected in 56,
heart and diaphragm in 17, diaphragm and tongue in 13, and heart
and tongue in 12 cattle. This study demonstrated a high level of
toxoplasma infection in slaughtered cattle in Jahrom and these
should be considered as one of the main sources of infection
for human in the region that requires attention and suggest that
some hygienic planning should be taken to control and prevent this
disease.
Recent Publications
1. Rezanezhad H, Sayadi F, Shadmand E, Nasab S D, Yazdi
H R, Solhjoo K, Kazemi A, Maleki M and Vasmehjani A
A (2017) Seroprevalence of
Toxoplasma gondii
among
HIV Patients in Jahrom, Southern Iran. Korean Journal
of Parasitology 55(1):99-103.
2. Azizi H, Shiran B, Boroujeni A B and Jafari M (2014)
Molecular survey of
Toxoplasma gondii
in sheep,
cattle and meat products in Chaharmahal va Bakhtiari
Province, Southwest of Iran. Iran Journal of Parasitology
9(3):429-34.
3. Ge W, Sun H, Wang Z, Xu P, Wang W, Mu G, Wei F and Liu
Q (2014) Prevalence and genotype of
Toxoplasma gondii
infection in cattle from Jilin Province, northeastern
China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Disease 14(6):399-402.
4. Asgari Q, Sarnevesht J, Kalantari M, Sadat S J,
Motazedian M H and Sarkari B (2011) Molecular survey
of toxoplasma infection in sheep and goat from Fars
province, Southern Iran. Tropical Animal Health and
Production 43(2):389-92.
5. Berger-Schoch A E, Herrmann D C, Schares G, Müller N,
Bernet D, Gottstein B and Frey C F (2011) Prevalence
and genotypes of
Toxoplasma gondii
in feline faeces
(oocysts) and meat from sheep, cattle and pigs in
Switzerland. Veterinary Parasitology 177(3-4):290-7.
Biography
Hassan Rezanezhad has completed his PhD degree from the University of Cam-
erino, Italy. His doctoral dissertation was focused on the study of cellular-mo-
lecular apoptosis-like cell death in
Plasmodium
. He is interested in studying
protozoa. He also has experiences in the fields of isolation and identification
of
Leishmania
and
toxoplasma
from patients by different techniques. His job
experiences include working in the medical laboratory for more than ten years.
rezasiv@gmail.comPrevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in slaughtered
cattle from Jahrom, Fars province, Southern Iran
Hassan Rezanezhad, Razieh Fazel, Kavous Solhjoo, Belal Armand
and
Masoud
Esmi Jahromi
Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Hassan Rezanezhad et al., J Prev Infect Cntrol 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9668-C1-003
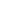
Figure 1:
PCR amplification products of Toxoplasma gondi SAG2 gene among
cattle’s tissue sample Lane L, molecular marker (GeneRuler TM 100 bp Plus DNA
Ladder, Fermentas UAB, Vilnius, Lithuania); 1, Negative control (DNA of Toxoplas-
ma gondi); lane 3-6(221 bp), positive samples.