Crystallography 2018
Structural Chemistry & Crystallography Communication
ISSN: 2470-9905
Page 23
June 04-05, 2018
London, UK
3
rd
Edition of International Conference on
Advanced Spectroscopy,
Crystallography and Applications
in Modern Chemistry
T
ri glycine sulphate (NH
2
CH
2
COOH)
3
.(H
2
SO
4
) (TGS) is a
ferroelectric and pyroelectric crystal which is mainly
used for infrared detector applications. The b axis of TGS is
the ferroelectric axis (axis of spontaneous polarization) and
along this axis it exhibits maximum pyroelectric coefficient of
~ 3 × 10-2 μC cm-2 K-1 at room temperature [1]. Due to this
reason the (010) face assumes importance in the morphology
of TGS crystal. The work described in the present report is
an attempt to study the evolution of the morphology of TGS
crystal in general and (010) face area relative to other faces
in particular and also to characterize the grown crystal for its
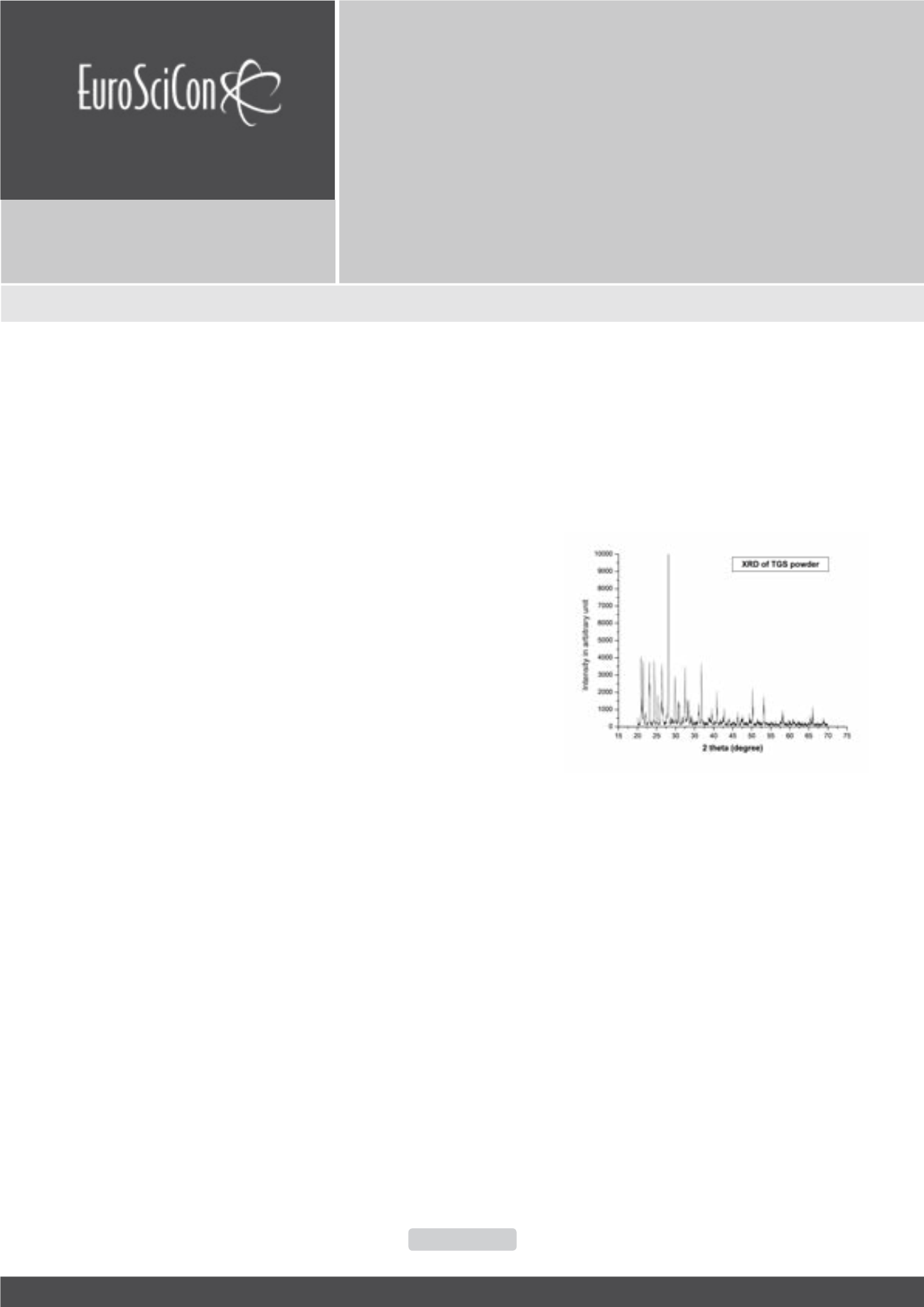
phase and optical homogeneity using X-ray diffraction and
optical interferometric techniques. Also to study the effect of
dopping of TGS with potassium succinate. TGS is known to
undergo a second order (order-disorder type) continuous phase
transition at the Curie temperature (Tc) of 49°C. Below this
temperature the crystal exhibits ferroelectric phase whereas
above it the crystal gets transformed to the paraelectric phase
[2]. It belongs to monoclinic system below and above the Curie
temperature. It has space group P21 in the ferroelectric phase
and cento-symmetric space group P21/m in the paraelectric
phase [3]. The lattice parameters of TGS are a=9.41Å, b=12.64
Å, c=5.73 Å and β=110°23’ [4]. Due to its self poling nature it
does not require any specific poling when it is cooled from
the high temperature phase to the low temperature one.
Taking advantage of this characteristic of TGS, and the fact
that across the Curie temperature the dipole moments of the
domains will behave differently which will influence the growth
rate of the (010) polar face, we have attempted to grow TGS
crystal . The morphology of TGS crystal in general and (010)
face in particular is studied. Also we attempted to study doping
induced morphological changes of TGS using Potassium
Succinate as dopant.
Recent Publications
1. Vijeesh P, Dr. Annieta Philip K, Dr. Supriya M.H (2016)
Growth and growth rate analysis of potassium
succinate crystal. N.S.C.G.A, Bhabha Atomic Research
Center, Mumbai, India
2. Vijeesh P, Paulbert Thomas, Dr. Annieta Philip and
Dr. Supriya M.H (2016), Growth rate analysis and
material characterization of potassium succinate
crystal. Smart Materials for Futuristic Electronics
and Communication Technology, The Cochin College,
Kochi-2.
Biography
Vijeesh P has his expertise in synthesis and characterization of Non linear
optical materials and their characterization. He designed a crystallizer for
slow cooling solution growth for the synthesis of the materials. And also
designed a temperature controller for slow cooling of the solution. He is an
Assistant Professor in Physics, Department of Physics, The Cochin College,
India. He presently doing his research in Department of Electronics , The
Cochin University of Science and Technology. He got slected for research
fellowships by Indian Academy of Science and did research work in Raja
Ramanna Center for Advanced Technology, India.
namastheviji@yahoo.co.inSYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TRIGLYCINE SULPHATE CRYSTALS
DOPED WITH POTASSIUM SUCCINATE
Vijeesh Padmanabhan
The Cochin College, India
Vijeesh Padmanabhan, Struct Chem Crystallogr Commun 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.21767/2470-9905-C1-005