Volume 3, Issue 2 (Suppl)
Trends in Green chem
ISSN: 2471-9889
Environmental & Green Chemistry 2017
July 24-26, 2017
Page 105
5
th
International Conference on
6
th
International Conference on
July 24-26, 2017 Rome, Italy
Environmental Chemistry and Engineering
Green Chemistry and Technology
&
Efficient extraction and functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals through hydrochloric acid
hydrolysis under hydrothermal conditions
Miao Cheng
and
Zongyi Qin
Donghua University, China
A
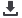
facile and efficient approach to prepare cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) is presented through hydrothermal procedure by
using inorganic chlorides as catalyst. The role of inorganic chlorides including ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl
3
•6H
2
O),
copper chloride dihydrate (CuCl
2
•2H
2
O), aluminum chloride (AlCl
3
) and manganese chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl
2
•4H
2
O)
played on the extraction and properties of high quality CNCs were determined. It is observed that the introduction of inorganic
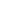
chlorides obviously enhanced the hydrolysis process through faster degradation of disordered region of cellulose. Compared
with those for pure hydrochloric acid hydrolysis, smaller diameter and larger length to diameter ratio of CNCs could be
obtained through salt–catalyzed hydrolysis. In addition, carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals (CCNCs) could be obtained by
a similar one−step procedure through a mixed acid system of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid (HCl/HNO
3
). It is found that
the addition of nitric acid could not only promote the conversion of surface groups on the CNCs, but also have significant
influences on the yield, particle size and microstructure of CNCs. For the volume ratio of HCl/HNO
3
of 7:3, the as−prepared
CCNCs exhibited the largest length to diameter ratio and narrowest dimension distributions as well as maximum degree of
oxidation of 0.12. Furthermore, high dispersion stability for the CCNCs could be observed due to the existence of negative
carboxyl groups. These results show that the using of salt–catalyzed hydrolysis especially ferric chloride has a significant
improvement on achieving high quality CNCs and the mixed acid system treatment could greatly simplify the preparation of
CCNCs with high yield and high crystallinity under mild hydrothermal conditions.
Biography
Miao Cheng is a student at College of Materials Science and Engineering at Donghua University. His research interests involve the sustainable production of
materials from biomass, development of high performance nanocomposites with the incorporation of cellulose nanocrystals, extraction and functionalization of
cellulose nanocrystals, and all-cellulose nanocomposites.
chengmiao91@126mail.comMiao Cheng et al., Trends in Green chem, 3:2
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9889-C1-003