Page 31
Volume 4
Journal of HIV & Retro Virus
STD 2018
December 03-04, 2018
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
December 03-04, 2018 Toronto, Canada
2
nd
International Conference on
Antibiotics for treating urogenital
Chlamydia trachomatis
infection in men and non-pregnant women
Carol Paez-Canro
1
, Jorge Andres Rubio-Romero
1
, Hernando G Gaitan
1
, Juan Pablo Alzate
2
, Lina M Gonzalez
2
and Anne Lethaby
3
1
Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Colombia
2
Fundacion Universitaria de Ciencias de la Salud, Colombia
3
University of Auckland, New Zealand
Background &Aim:
The genital infection caused by
Chlamydia trachomatis
(CT) is one of the most common Sexually Transmitted
Diseases (STDs) globally. Different antibiotics regimens are recommended in Clinical Practice Guidelines (CPG) for CT urogenital
infections. The study aims to assess the efficacy and safety of antibiotic treatment for
Chlamydia trachomatis
genital infection in
men and non-pregnant women.
Method:
We developed the electronic searches in (CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase and LILACS) and two trials registers. Selection
criteria, we included randomized controlled trials of sexually-active non-pregnant women and men with genital CT infection. We
estimated the pooled risk ratio.
Result:
Our primary outcomes were microbiological failure and adverse events. We selected 14 studies. For Azithromycin vs.
Doxycycline in women treated for CT, the effect on microbiological failure was uncertain (RR=1.71, 95%, CI 0.48 to 6.16). In men
treated for CT, the risk of microbiological failure was probably higher with Azithromycin compared to Doxycycline (RR 2.45, 95%
CI, 1.36 to 4.41). We found that Azithromycin probably has less adverse events in both genders compared to Doxycycline (RR 0.83,
95% CI, 0.73 to 0.95; I2=0%). For tetracyclines vs. Quinolones, the effect of Doxycycline compared to Ofloxacin on microbiological
failure in women was not estimable and the effect of Doxycycline vs. Ofloxacin also in women on clinical failure was uncertain
(RR 0.94, 95% CI 0.39 to 2.25). For men treated for CT the effect of Doxycycline compared to Ofloxacin at the same doses on
microbiological failure was uncertain (RR 8.53, 95% CI 0.43 to 167.3).
Conclusion:
Regimens with Azithromycin 1 gram single oral dose has probably less efficacy than doxycycline 100 mg twice a day
for seven days in men in terms of microbiological failure. However, in men there might be little or no differences in terms of clinical
failure.
Biography
Juan Pablo Alzate is a Medical Doctor graduated from the National University of Colombia. He has completed his Master’s degree in Clinical Epidemiology from
the National University of Colombia. He is currently an Assistant Instructor in the Research Division .
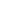
jpalzategr@fucsalud.edu.comFigure 1.
Forest plot of comparison 1. Macrolides. Regimens with azithromycin: azithromycin 1 g-only dose vs doxycycline
100 mg twice a day for 7 days, outcome: 1.1 microbiological failure.
Carol Paez-Canro et al., J HIV Retrovirus 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9676-C2-006