Trends in Green Chemistry
ISSN: 2471-9889
October 05-06, 2018
Barcelona, Spain
Renewable Energy 2018
Page 12
2
nd
Edition of Global Summit on
Renewable Energy &
Emerging Technologies
Biomass conversion to fuels and value-added
chemicals with magnetically recoverable
catalysts
Lyudmila M Bronstein
Indiana University, USA
Lyudmila M Bronstein, Trends in Green chem 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9889-C3-013
B
iomass conversion plays a tremendous role in obtaining
value-added chemicals and fuels from renewable sources
without use of petrochemicals. In the last decade magnetically
recoverablecatalystshave receivedconsiderableattentiondue to
more environmentally friendly processes, conservationof energy,
and cheaper target products. In this talk author will discuss the
use of magnetically recoverable catalysts for biomass and biooil
related processes, including transformations of cellulose to
value-added chemicals, syngas (produced by bio-oil pyrolysis) to
methanol and methanol to hydrocarbons (fuels) as well as bio-
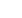
oil hydrogenation to important chemicals. Figure 1 shows high
resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) image
of the magnetic zeolite containing Ni nanoparticles (left), its
energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) map (superposition of Fe
and Ni maps, center), and the methanol-to-hydrocarbon (MTH)
reaction pathway (right). Modifying the iron oxide (magnetite,
Fe
3
O
4
) amounts, we were able to control the catalyst activity and
the product distribution inMTH. Themodification of zeoliteswith
Ni nanoparticles allowed us to significantly improve the catalyst
stability due to diminishing coke formation and disordering
of the coke formed. As is relevant to many catalytic systems,
it will be demonstrated that the presence of magnetic iron
oxide nanoparticles can enhance catalytic activity or change
the reaction mechanism, allowing for more valuable products.
In some instances, however, the presence of iron oxide can
be detrimental due to side reactions. In such a case, a proper
iron oxide nanoparticle protection/stabilization is required to
suppress side reactions.
Figure 1:
HRTEM image (left) and superposition of Fe and Ni EDS maps
(center) of themagnetic zeolitewithNi nanoparticles and theMTH reaction
pathway (right)
Recent Publications
1. DasVK, ShifrinaZBandBronstein LM(2017) Graphene
and graphene-like materials in biomass conversion:
paving the way to the future. Journal of Materials
Chemistry 5:25131.
2. Oracko T
et al.
(2017) Metal ion distribution and
oxygen vacancies determine activity of magnetically
recoverable catalysts in methanol synthesis. ACS
Applied Materials & Interfaces 9:34005.
3. Cherkasov N
et al.
(2017) Hydrogenation of bio-oil
into higher alcohols over Ru/Fe
3
O
4
-SiO
2
catalysts. Fuel
Processing Technology 167:738.
4. Alibegovic K
et al.
(2017) Furfuryl alcohol synthesis
from furfural over magnetically recoverable catalysts:
does the catalyst stabilizingmediummatter? Chemistry
Select 2:5485.