E u r o S c i C o n J o i n t E v e n t o n
Laser Optics & Photonics and
Atomic & Plasma Science
American Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology
ISSN: 2349-3917
J u l y 1 6 - 1 7 , 2 0 1 8
P r a g u e , C z e c h R e p u b l i c
Page 21
Laser Optics & Photonics and Atomic & Plasma Science 2018
O
ne of the main research activities of the Sol-Gel Group at Madrid (
GSG-ICMM
)
is based on a new approach of incorporating electroactive organic molecules
in glasses. In other words, the possibility of manipulating the optical properties
of molecules encapsulated in thin-films glasses by means of application of an
external electric field. Due to their interesting optical properties, these new
materials can be used in a very wide range of applications. This development
consists on themicroencapsulation of liquid crystal (LC) droplets dispersed in Sol-
Gel glasses. The prototypes of optical switches have been developed as GDLC
®
(Gel-glass Dispersed Liquid Crystal). As an interesting alternative, the structure of
biological templates has been also explored as a novel route for the preparation
of an electro optical device from a biofilm structure created by bacterial activity.
Biofilms created by livemicroorganisms can provide specific structures. The novel
usage of the tridimensional architecture and optical properties of a biofilmcreated
by the bacterium
Pseudomonas putida
mt-2 for the fabrication of a variable light-
transmission device will be described. The bacterial cell factory is a promising
non-chemical route for the generation of tridimensional structures oriented to
the design of new. A new concept of an optical thin-film material that exhibits
reversible humidity-responsive light-transmittance properties is presented. The
novel reversible humidity-responsive light transmission thin-filmmaterial consists
on a dispersive porous structure, with embedded hygroscopic and deliquescent
compounds, that is able to scavenge water molecules from humid air to fill-up
the pores and become transparent to the incident light. Upon exposure to dry air,
water is released from the structure and the material recovers its original light
scattering properties. The developed thin-films can change their transparency
when exposed to air with different relative humidity (RH), adjusting the light
throughput. Therefore, this material concept can be used to design new optical
windows, having the advantage that they do not require liquid crystal, transparent
conductive glass substrates or complex layer-by-layer architectures for operation
as in conventional smart windows. The general design of the humidity-driven light-
scattering device concept will be presented.
Biography
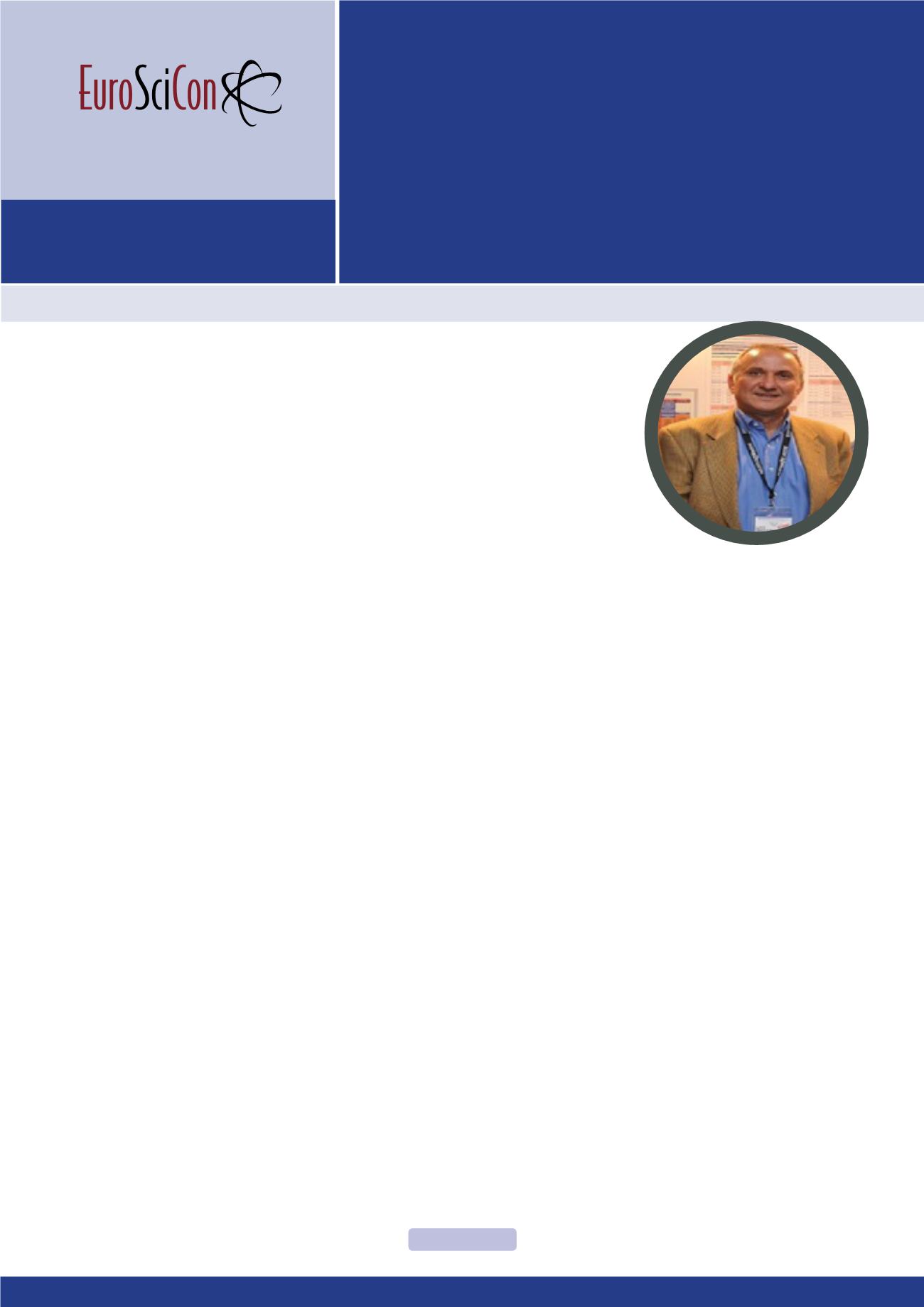
D Levy has started (1982-89) at The Hebrew University of Je-
rusalem, with the pioneering first application of the Sol-Gel pro-
cess to the preparation of organically doped silica gel-glasses
and reached the ICMM-CSIC in 1989. He was awarded the First
Ulrich Prize for the most innovative work and was nominated
to the Juan Carlos I Rey research award. He has authored over
133 papers (> 6800 citations; h=40, G-Scholar), reviews, book
chapters, Co-Editor of The Sol-Gel Handbook, and several pat-
ents, and was PI for 27 Industry Projects. He is member of the
International Advisory Board of the Sol-Gel Optics and Optoelec-
tronics and Optical Science and Technology of the SPIE (USA),
and a Member of the Experts Panel of the FP7 and H2020
Materials and Space Programs. He Chaired the XVII Sol-Gel
International Conference in Madrid, 2013. He is a Professor at
ICMM-CSIC heading the Sol-Gel Group (
SGG
) and his research
interests are optical materials and their applications, and also
headed the LINES of the INTA, where developed space mate-
rials for space optical instruments, able to be implemented on
the board of a satellite.
David.Levy@icmm.csic.esSol-gel Materials for Optical Applications
D Levy
2
, E Castellon
1
and M Zayat
2
1
CIEMTEC-Universidad Costa Rica, CR
2
ICMM-CSIC, Spain
D Levy et al., Am J Compt Sci Inform Technol 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.21767/2349-3917-C1-001