Volume 3, Issue 2 (Suppl)
Trends in Green chem
ISSN: 2471-9889
Environmental & Green Chemistry 2017
July 24-26, 2017
Page 16
5
th
International Conference on
&
6
th
International Conference on
July 24-26, 2017 Rome, Italy
Green Chemistry and Technology
Environmental Chemistry and Engineering
Novel heterogeneous catalysts and processes for biomass derivatives transformations into fuels and
chemicals
A
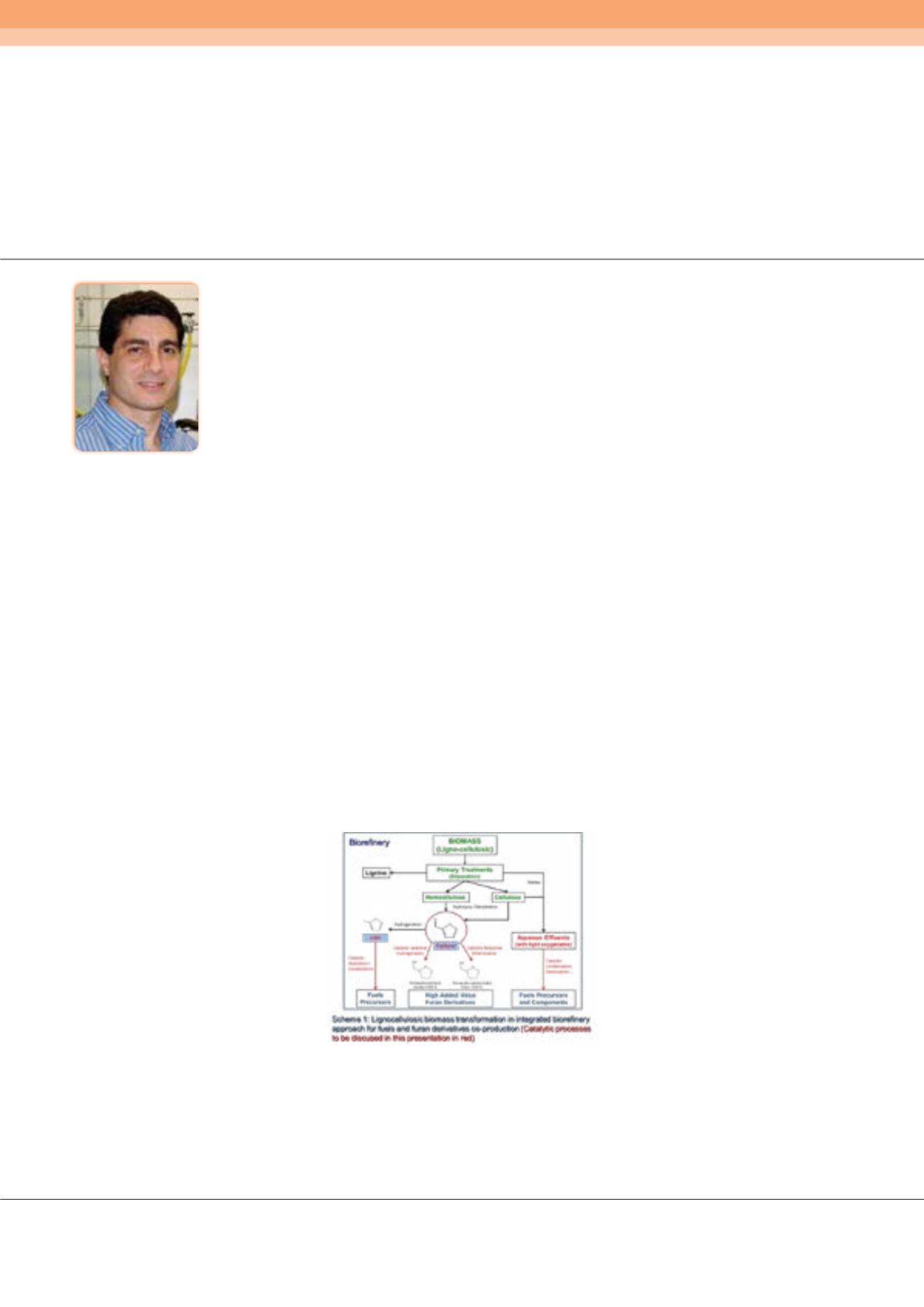
wide range of renewable raw materials and products can be easily obtained from ligno-cellulosic biomass and their
derivatives in both polymeric (i.e. cellulose, starch, lignin) and monomeric (i.e. sugars, polyols, phenols) forms. These bio-
based platform compounds could be converted into a large variety of chemical products and fuels to replace non-renewable
fossil raw materials. The attainment of these bio-products is environmentally more favorable than that of their petroleum
derived analogues, but also more expensive due to the lack of simple and efficient synthesis processes. In this sense, it is
necessary to develop new highly selective catalytic processes allowing obtaining these bio-products in a competitive way (with
lower energy consumption and higher profits) compared to conventional petro-products. Aligned with the new bio-economy
and zero-waste concepts, the new bio-refineries should produce these bio-products for fuels and chemicals applications by
reducing wastes, this includes both decreasing of side-products formation and residual effluents valorization in an integrated
approach. In this presentation, the application of novel solid catalysts (with well controlled acid/base and redox properties)
recently developed at ITQ for the efficient transformation of biomass derivatives into high added value products will be assessed.
Particularly, catalytic processes for the production of chemicals starting from furfural will be discussed, such as i) the selective
hydrogenation of furfural to tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol, and ii) the reductive etherification of furfural to tetrahydrofurfuryl
alkyl-ethers. In addition, solid catalysts will be evaluated in the production of precursors and components for fuels, such as iii)
the hydrolysis/condensation of 2-methyl-furan, and iv) the valorization of oxygenated compounds present in biomass-derived
aqueous fractions via ketonization/condensation, among others.
Biography
Marcelo E Domine completed his PhD at the Polytechnic University of Valencia (Spain) in 2003 under the guidance of Prof.ACorma, and Postdoctoral Studies at the IRCE-
LYON - CNRS (France, 2005-07). In 2008, he re-joined the Instituto de Tecnología Química (UPV-CSIC) of Valencia, Spain as Scientific Researcher of CSIC. His current
research involves the synthesis and characterization of solid catalysts and their application in sustainable chemical processes, mainly focusing on new biomass-derivatives
transformations and wastes valorization into fuels and valuable chemicals. He is co-author of more than 55 publications (also including several patent applications). He has
presented at over 18 invited conferences around the world. He has acted as Guest Managing Editor of
Catalysis Today
, and also as Reviewer in many renowned scientific
journals in catalysis and fuels areas. He is actually the representative of CSIC (Spain) at the EERA Program – JP-Bioenergy (European Commission).
mdomine@itq.upv.esMarcelo E Domine
Instituto de Tecnología Química (UPV - CSIC), Spain
Marcelo E Domine, Trends in Green chem, 3:2
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9889-C1-001