E u r o S c i C o n C o n f e r e n c e o n
Nanotechnology &
Smart Materials
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN 2471-9838
O c t o b e r 0 4 - 0 6 , 2 0 1 8
Am s t e r d a m , N e t h e r l a n d s
Nanotechnology & Smart Materials 2018
Page 35
N
anotechnology continuously reshapes our world, redefines and enriches
knowledge, while opening new horizons. Tailored construction materials have
become a reality and characterization techniques relating to all scales (nano-mi-
cro-macro) are being correlated. But what can nanotechnology offer in cement
science and how can we best utilize the available resources and expand them?
This talk provides an overview of the speaker’s latest achievements in the field
of cement science with the addition of specific nanoparticles. Silicon dioxide and
montmorillonite nanoparticles are scrutinized, new theories and methodologies
on how the dispersion medium and nanostructure of the particles can affect
the performance and characteristics of composite cement formulations are dis-
cussed. In light of the E U regulations on limiting the CO
2
emissions mainly caused
by the production of Portland cement clinker (PC), the research carried out breaks
the allowable minimum limits of PC addition in composite cement formulations.
The permissible maximum limits of additions such as fly ash, limestone and/or
silica fume according to EN 197-1:2011 are also broken by adding nanoparticles.
This breakthrough is allowing a twofold advantage in embodied CO
2
emissions
reduction and further financial savings. Denser microstructure, stronger and more
durable cementitious products are rendered possible. How can we best monitor
these changes? Of the various characterization techniques available, which can
be directly correlated? On top of all, what are the levels of confidence with respect
to the nanoparticles addition? Which are the controlling parameters and how can
we ascertain the benefit? In addition, could specific nanoparticles be suitable for
the structural restoration of historical listed monuments? All the above questions
will be answered through selected series of comparative results showing the en-
hancements offered by the addition of the nanoparticles and the difficulties en-
countered. The talk will be concluded with ideas on further research
Biography
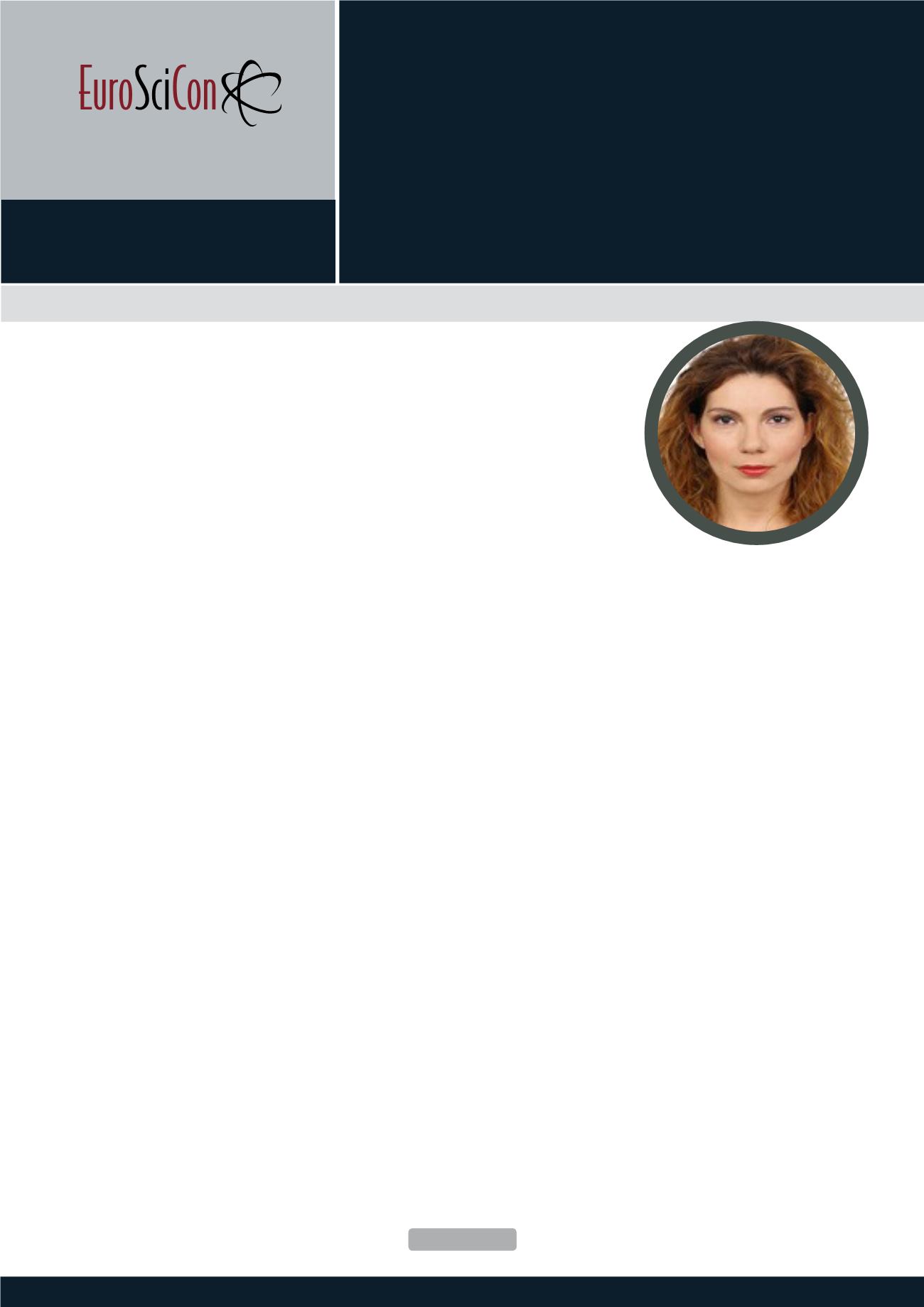
Styliani Papatzani has completed three Master courses [Imperi-
al College and National Technical University of Athens (NTUA)]
with awards and distinctions. She has worked in industry carry-
ing out structural design of newbuildings and structural assess-
ments of existing buildings and monuments, then completed a
PhD on the effect of various nanoparticles in cement formula-
tions from the University of Bath, UK and Postdoctoral studies
at the NTUA. She is currently a Senior Engineer at the Hellenic
Ministry of Culture, Greece and a Lecturer at the University of
Brighton, UK. She has publishedmore than 25 papers in reputed
journals, book chapters and conferences and has been serving
as a Consultant and Technical Expert in a number of profes-
sional committees.
spapatzani@culture.gr spapatzani@gmail.comNanotechnology: cementitious
nanocomposites and restoration materials
Styliani Papatzani
1
Hellenic ministry of culture and sports, Directorate of restoration of
medieval and post-medieval Monuments, Greece
2
University of Brighton, England
Styliani Papatzani, Nano Res Appl Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C6-024