 |
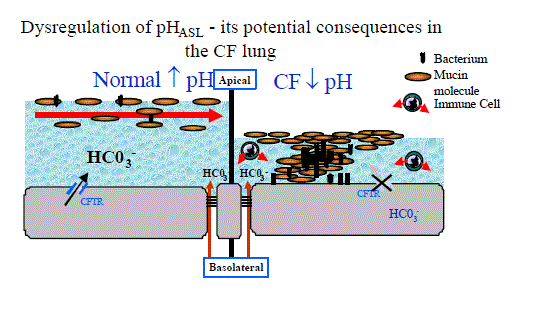
| Figure 2.Predicted adverse effects of reduced ASL pH on CF airway epithelium. On normal airway relatively higher pH results in a less viscous surface layer, facilitating transport of retained bacteria in the mucous layer in a cephalad directions. Putatively, in CF, lower pH results in an increasingly viscous "low-volume" gel, adherence of soluble and tethered mucins, resulting in mucous plaques, persistence of dysfunctional immune cells and bacteria.. |