 |
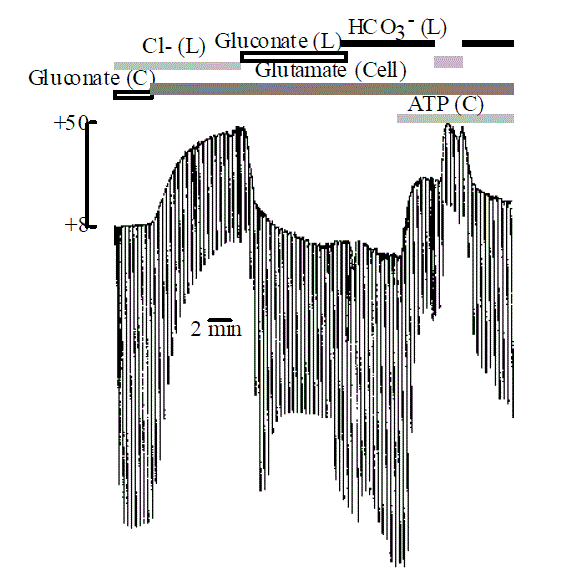
| Figure 2.The effect of glutamate on CFTR Cl- and HCO3 - conductances. In this experiment substituting glutamate for gluconate in the cytoplasmic bath resulted in a large increase in Cl- diffusion potential (generated by 140 mM Cl- in the lumen and 140 mM glutamate in the cytoplasmic bath) and conductance in the complete absence of cAMP and ATP. Notice that substituting luminal Cl- with impermeant anion gluconate reversed the anion diffusion potential to the junction potential values indicating that glutamate, in fact, activated Cl- conductance. In contrast, substituting HCO3 - for gluconate (in the lumen) in the presence of glutamate in the cytoplasmic bath had little effect on the anion diffusion potentials or conductance suggesting that glutamate alone did not activate CFTR HCO3 - conductance. However, addition of 5mM ATP to the cytoplasmic bath in the presence of glutamate resulted in a large increase in both HCO3 - and Cl- conductances as indicated by changes in the respective ion diffusion potentials and electrical conductances. |