 |
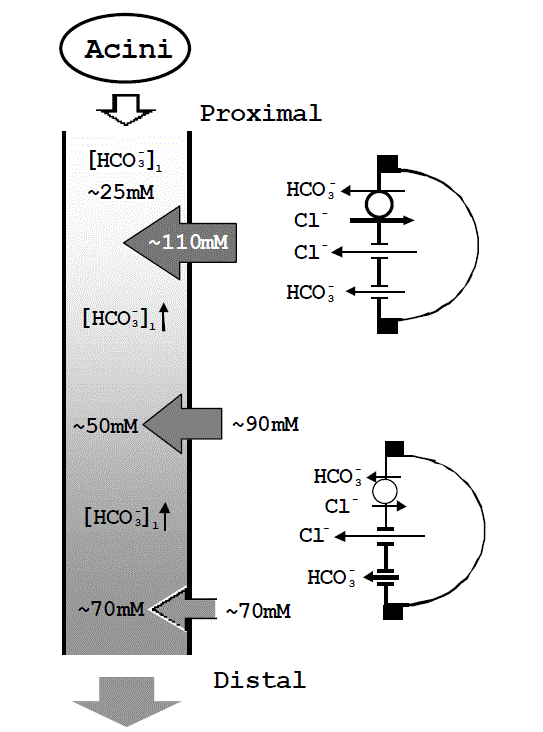
| Figure 2. Computer simulation of pancreatic ductal HCO3 - secretion using a simple Cl- channel/anion exchanger mechanism. (We have used network thermodynamics to construct a three compartment mathematical model that simulates an epithelial cell is situ within an intact duct [2]. The model is based on published experimental data on the duct cell. It provides information about secretory rate and the HCO3 - concentration in the secreted and luminal fluids, as well as transient and steady state data on intracellular pH and [Cl-]i, cell volume, membrane and transepithelial potentials, and the voltage divider ratio. The thickness of the arrows on the duct indicates the volume of fluid secreted at different levels in the ductal system. The length of the arrows on the cells indicates the activity of individual transport processes.) |