 |
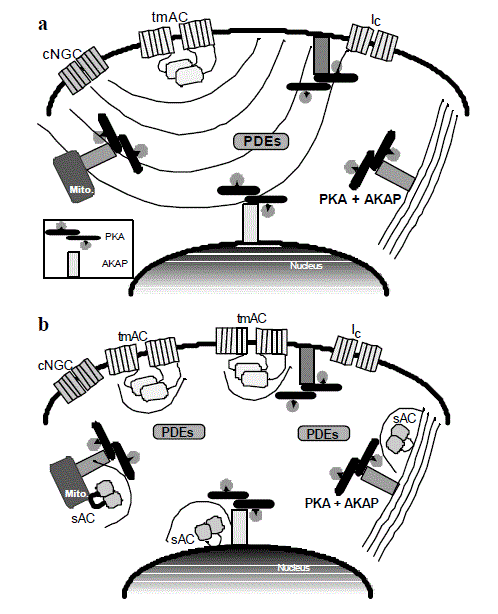
| Figure 3:Models of cAMP signal transduction. a) Previous models of cAMP signaling require the diffusion of cAMP from plasma membrane-localized tmACs to targets localized throughout the cell. These targets include effectors on the plasma membrane [cyclic nucleotide gated channels (cNGC) and channels activated by PKA (IC)] and tethered to a variety of intracellular sites (PKA bound to AKAPs). Diffusion of cAMP throughout the cytosol would likely diminish specificity, selectivity, and signal strength. This model is further complicated by the presence of phosphodiesterases (PDEs) which degrade cAMP preventing its diffusion. b) Cytosolic localization of sAC provides both specificity and selectivity by permitting generation of cAMP proximal to intracellular targets. Furthermore, this model for cAMP action incorporates PDEs, which would act to limit diffusion and prevent non-specific effector activation. |