 |
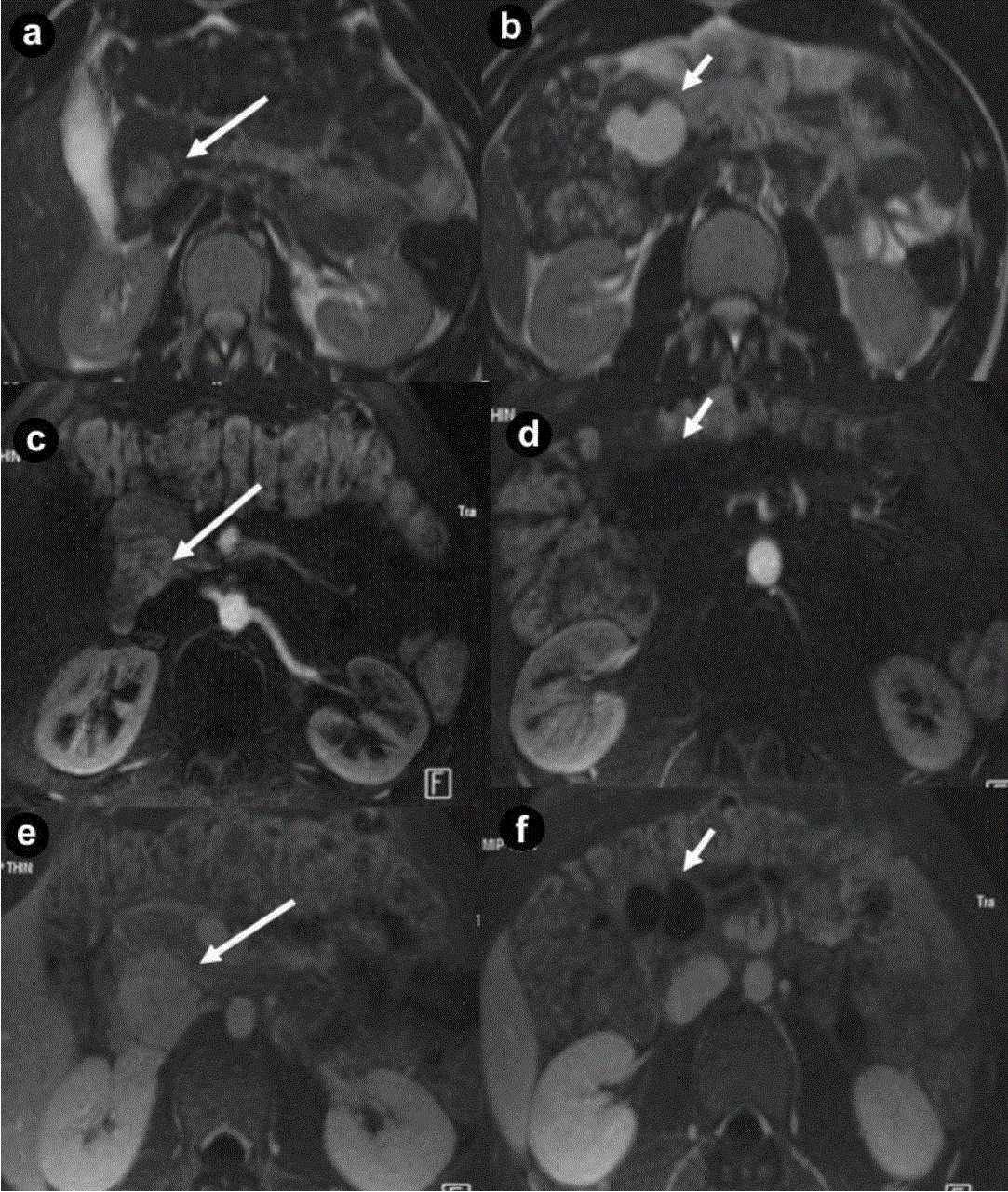
| Figure 3. Pancreatic non functioning neuroendocrine tumor and pancreatic serous cystadenoma in the same patient: asymptomatic 24-yearold man. Axial (a. b.) T2-weighted MR images, axial 3D volumetric gradient-echo T1-weighted fat suppressed images after intravenous contrast medium administration during arterial pancreatic (c. d.) and portal venous (e. f.) phases of contrastographic dynamic study. In pancreatic head a solid mass (a. arrow), heterogeneously hyperintense on T2-weighted MR images (a.) with homogeneous enhancement after intravenous contrast medium administration during arterial pancreatic phase of contrastographic dynamic study (c.), without washout in portal venous phase (e.) is present. In pancreatic head a cystic parenchymal lesion (short arrow), more hyperintense than solid mass, with fluid signal intensity on T2-weighted MR images (b.), without enhancement after intravenous contrast medium administration during arterial pancreatic (d.), and portal venous phases (f.), is visible. Inside the cystic lesion a septa is recognizable. Pancreaticoduodenectomy with Whipple procedure was performed. Histological specimen showed the presence of pancreatic macrocystic serous cystadenoma and non functioning neuroendocrine tumor of pancreatic head. |